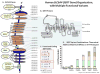
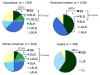
Human serotonin transporter gene (SLC6A4) variants: their contributions to understanding pharmacogenomic and other functional G×G and G×E differences in health and disease
- PMID: 21439906
- PMCID: PMC3487694
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coph.2011.02.008
Human serotonin transporter gene (SLC6A4) variants: their contributions to understanding pharmacogenomic and other functional G×G and G×E differences in health and disease
Abstract
Recent major findings from studies of SLC6A4 and its corresponding protein, the serotonin (5-HT) transporter (SERT) in humans, rodents and non-human primates indicate that combinations of SLC6A4 non-coding 5', 3' UTRs and intronic regions plus coding variants acting together can change 5HT transport as much as 40-fold in vitro. In vivo, SLC6A4 variants in humans and other species lead to marked physiological changes, despite mitigating neurodevelopmental adaptations in 5-HT receptors plus compensatory alterations in 5-HT synthesis and metabolism. Polymorphisms in SLC6A4 are associated with differences in emotional, endocrine, and personality characteristics as well as many diseases. This gene, in combinations with gene×gene (G×G) and gene×environment (G×E) interactions nonetheless remains incompletely understood, with some association findings remaining controversial. Considering its primary importance in the regulation and function of the entire serotonergic system (as evidenced by the consequences of SERT-mediated reuptake inhibition by SRIs like fluoxetine in humans and of genetically engineered changes in mice and rats), it seems likely that SLC6A4 and SERT will remain areas of high interest in our field's attempts to better understand and treat 5-HT-related disorders.
Copyright © 2011. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Lesch KP, Bengel D, Heils A, Sabol SZ, Greenberg BD, Petri S, Benjamin J, Muller CR, Hamer DH, Murphy DL. Association of anxiety-related traits with a polymorphism in the serotonin transporter gene regulatory region. Science. 1996;274:1527–1531. First full report of the consequences of the SLC6A4 5′ region 5HTLPR indel with effects on 3H-5HT uptake, mRNA and reporter gene expression changes plus differential allele associations with neuroticism and related personality traits in >600 individuals. - PubMed
-
- Hu XZ, Lipsky RH, Zhu G, Akhtar LA, Taubman J, Greenberg BD, Xu K, Arnold PD, Richter MA, Kennedy JL, et al. Serotonin transporter promoter gain-of-function genotypes are linked to obsessive-compulsive disorder. Am J Hum Genet. 2006;78:815–826. Discovery of a 5′ SNP modifying the SLC6A4 5HTLPR with combination alleles formed strongly associated with OCD in two large samples, plus explication of strong ethnic influences on allele distributions. - PMC - PubMed
-
- MacKenzie A, Quinn J. A serotonin transporter gene intron 2 polymorphic region, correlated with affective disorders, has allele-dependent differential enhancer-like properties in the mouse embryo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96:15251–15255. First description of a functional Stin2 SLC6A4 variant now associated with multiple disorders. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ozaki N, Goldman D, Kaye WH, Plotnicov K, Greenberg BD, Lappalainen J, Rudnick G, Murphy DL. Serotonin transporter missense mutation associated with a complex neuropsychiatric phenotype. Mol Psychiatry. 2003;8:933–936. - PubMed
-
- Prasad HC, Zhu CB, McCauley JL, Samuvel DJ, Ramamoorthy S, Shelton RC, Hewlett WA, Sutcliffe JS, Blakely RD. Human serotonin transporter variants display altered sensitivity to protein kinase G and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:11545–11550. Detailed explication of SLC6A4 coding region variants and their regulation. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources