Thermodynamics of monolayers formed by mixtures of phosphatidylcholine/phosphatidylserine
- PMID: 21440423
- PMCID: PMC3081974
- DOI: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2011.02.037
Thermodynamics of monolayers formed by mixtures of phosphatidylcholine/phosphatidylserine
Abstract
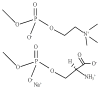
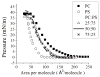
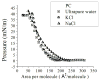
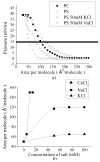
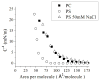
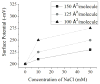
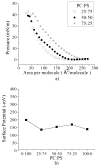
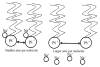
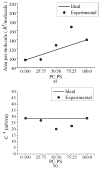
In this work we obtain the thermodynamic properties of mixed (1-stearoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine) PC and (1-stearoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-l-serine (sodium salt)) PS monolayers. Measurements of compressibility (isotherms, bulk modulus, and excess area per molecule) and surface potential show that the properties of monolayers at the air-water interface depend on the concentration of ions (Na(+) and K(+)) and the proportion of PS in the mixture. The dependence on PS arises because the molecule is originally bound to a Na(+) counterion; by increasing the concentration of ions the entropy changes, creating a favorable system for the bound counterions of PS to join the bulk, leaving a negatively charged molecule. This change leads to an increase in electrostatic repulsions which is reflected by the increase in area per molecule versus surface pressure and a higher surface potential. The results lead to the conclusion that this mixture of phospholipids follows a non ideal behavior and can help to understand the thermodynamic behavior of membranes made of binary mixtures of a zwitterionic and an anionic phospholipid with a bound counterion.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Alberts B. Molecular biology of the cell. Garland Science; 2007.
-
- Cevc G. Phospholipids handbook. CRC Press; 1993.
-
- Mattai J, Hauser H, Demel RA, Shipley GG. Interactions of metal ions with phosphatidylserine bilayer membranes: effect of hydrocarbon chain unsaturation. Biochem. 1989;28:2322–2330. - PubMed
-
- Langner M, Kubica K. The electrostatics of lipid surfaces. Chem Phys Lipids. 1999;101:3–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

