Potent inhibitors of hepatitis C core dimerization as new leads for anti-hepatitis C agents
- PMID: 21440437
- PMCID: PMC3086078
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2011.03.014
Potent inhibitors of hepatitis C core dimerization as new leads for anti-hepatitis C agents
Abstract
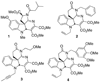
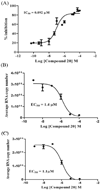
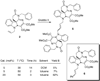
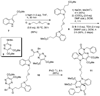
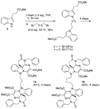
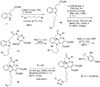
New indoline alkaloid-type compounds which inhibit HCV production by infected hepatoma cells have been identified. These compounds, dimeric-type compounds of previously known inhibitors, display double digit nanomolar IC(50) and EC(50) values, with cytotoxicity CC(50) indexes higher than 36 μM, thus providing ample therapeutic windows for further development of HCV drugs.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Direct binding of a hepatitis C virus inhibitor to the viral capsid protein.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e32207. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032207. Epub 2012 Feb 28. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22389688 Free PMC article.
-
New small molecule inhibitors of hepatitis C virus.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2009 Dec 15;19(24):6926-30. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2009.10.070. Epub 2009 Oct 21. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2009. PMID: 19896376 Free PMC article.
-
Peptide inhibitors of hepatitis C virus core oligomerization and virus production.J Gen Virol. 2009 Jun;90(Pt 6):1319-1328. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.008565-0. Epub 2009 Mar 4. J Gen Virol. 2009. PMID: 19264632
-
Alkaloid and benzopyran compounds of Melicope latifolia fruit exhibit anti-hepatitis C virus activities.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021 Jan 12;21(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s12906-021-03202-8. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021. PMID: 33435968 Free PMC article.
-
Design, Synthesis and Structure-Activity Relationship Optimization of Lycorine Derivatives for HCV Inhibition.Sci Rep. 2015 Oct 7;5:14972. doi: 10.1038/srep14972. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26443922 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Direct binding of a hepatitis C virus inhibitor to the viral capsid protein.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e32207. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032207. Epub 2012 Feb 28. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22389688 Free PMC article.
-
Access to pyrrolo-pyridines by gold-catalyzed hydroarylation of pyrroles tethered to terminal alkynes.Beilstein J Org Chem. 2011;7:1468-74. doi: 10.3762/bjoc.7.170. Epub 2011 Oct 26. Beilstein J Org Chem. 2011. PMID: 22238519 Free PMC article.
-
Current and future therapies for hepatitis C virus infection.N Engl J Med. 2013 May 16;368(20):1907-17. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1213651. N Engl J Med. 2013. PMID: 23675659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HCV core protein and virus assembly: what we know without structures.Immunol Res. 2014 Oct;60(1):1-10. doi: 10.1007/s12026-014-8494-3. Immunol Res. 2014. PMID: 24557493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the Virus Capsid as a Tool to Fight RNA Viruses.Viruses. 2022 Jan 18;14(2):174. doi: 10.3390/v14020174. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35215767 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
-
For some reviews of hepatitis C: Bartenschlager R, Lohmann V. J. Gen. Virol. 2000;81:1631. Giannini C, Brechot C. Cell Death Diff. 2003;10:S27. Simmonds P. J. Gen. Virol. 2004;85:3173. Alter MJ. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007;13:2436..
-
-
- Lavanchy D. Liver Int. 2009;29:74. - PubMed
-
-
For reviews: Chen KX, Njoroge FG. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs. 2009;10:821. Chary A, Holodniy M. Rev. Rec. Clin. Trials. 2010;5:158..
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

