STAT3 signaling: anticancer strategies and challenges
- PMID: 21441118
- PMCID: PMC3063716
- DOI: 10.1124/mi.11.1.4
STAT3 signaling: anticancer strategies and challenges
Abstract
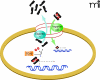
Multiple lines of evidence place STAT3 at a central node in the development, progression, and maintenance of many human tumors, and STAT3 has been validated as an anti-cancer target in several contexts. STAT3 modulates the transcription of a variety of genes involved in the regulation of critical functions, including cell differentiation, proliferation, apoptosis, angiogenesis, metastasis, and immune responses. For many cancers, elevated levels of activated STAT3 have been associated with a poor prognosis. We review approaches that have been pursued to target STAT3, and we highlight some of the promises and challenges associated with developing an anticancer drug that might therapeutically inhibit the STAT3 signaling pathway.
Figures
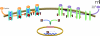
References
-
- Leeman RJ, Lui VW, Grandis JR. (2006) STAT3 as a therapeutic target in head and neck cancer. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 6:231–241 - PubMed
-
- Quesnelle KM, Boehm AL, Grandis JR. (2007) STAT-mediated EGFR signaling in cancer. J Cell Biochem. 102:311–319 - PubMed
-
- Frank DA. (2007) STAT3 as a central mediator of neoplastic cellular transformation. Cancer Letters. 251:199–210 - PubMed
-
- Germain D, Frank DA. (2007) Targeting the cytoplasmic and nuclear functions of signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 for cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 13:5665–5669 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
