The RNA worlds in context
- PMID: 21441585
- PMCID: PMC3385955
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a006742
The RNA worlds in context
Abstract
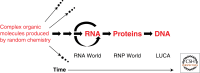
There are two RNA worlds. The first is the primordial RNA world, a hypothetical era when RNA served as both information and function, both genotype and phenotype. The second RNA world is that of today's biological systems, where RNA plays active roles in catalyzing biochemical reactions, in translating mRNA into proteins, in regulating gene expression, and in the constant battle between infectious agents trying to subvert host defense systems and host cells protecting themselves from infection. This second RNA world is not at all hypothetical, and although we do not have all the answers about how it works, we have the tools to continue our interrogation of this world and refine our understanding. The fun comes when we try to use our secure knowledge of the modern RNA world to infer what the primordial RNA world might have looked like.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
