Comparative advantages of mechanical biosensors
- PMID: 21441911
- PMCID: PMC3839312
- DOI: 10.1038/nnano.2011.44
Comparative advantages of mechanical biosensors
Abstract
Mechanical interactions are fundamental to biology. Mechanical forces of chemical origin determine motility and adhesion on the cellular scale, and govern transport and affinity on the molecular scale. Biological sensing in the mechanical domain provides unique opportunities to measure forces, displacements and mass changes from cellular and subcellular processes. Nanomechanical systems are particularly well matched in size with molecular interactions, and provide a basis for biological probes with single-molecule sensitivity. Here we review micro- and nanoscale biosensors, with a particular focus on fast mechanical biosensing in fluid by mass- and force-based methods, and the challenges presented by non-specific interactions. We explain the general issues that will be critical to the success of any type of next-generation mechanical biosensor, such as the need to improve intrinsic device performance, fabrication reproducibility and system integration. We also discuss the need for a greater understanding of analyte-sensor interactions on the nanoscale and of stochastic processes in the sensing environment.
Figures


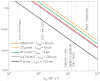
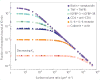


References
-
- Braun T, et al. Quantitative time-resolved measurement of membrane protein- ligand interactions using microcantilever array sensors. Nature Nanotech. 2009;4:179–185. - PubMed
-
- Phelan ML, Nock S. Generation of bioreagents for protein chips. Proteomics. 2003;3:2123–2134. - PubMed
-
- Backmann N, et al. A label-free immunosensor array using single-chain antibody fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:14587–14952. The authors use a microcantilever with static-mode defection to achieve a sensitivity of≈1 nM, and include a detailed discussion of device functionalization. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Waggoner PS, Varshney M, Craighead HG. Detection of prostate specific antigen with nanomechanical resonators. Lab Chip. 2009;9:3095–3099. The authors report femtomolar detection from serum through fluid phase capture and detection in vacuo. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

