Cadmium-Induced Disruption in 24-h Expression of Clock and Redox Enzyme Genes in Rat Medial Basal Hypothalamus: Prevention by Melatonin
- PMID: 21442002
- PMCID: PMC3062465
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2011.00013
Cadmium-Induced Disruption in 24-h Expression of Clock and Redox Enzyme Genes in Rat Medial Basal Hypothalamus: Prevention by Melatonin
Abstract
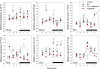
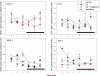
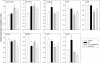
In a previous study we reported that a low daily p.o. dose of cadmium (Cd) disrupted the circadian expression of clock and redox enzyme genes in rat medial basal hypothalamus (MBH). To assess whether melatonin could counteract Cd activity, male Wistar rats (45 days of age) received CdCl(2) (5 ppm) and melatonin (3 μg/mL) or vehicle (0.015% ethanol) in drinking water. Groups of animals receiving melatonin or vehicle alone were also included. After 1 month, MBH mRNA levels were measured by real-time PCR analysis at six time intervals in a 24-h cycle. In control MBH Bmal1 expression peaked at early scotophase, Per1 expression at late afternoon, and Per2 and Cry2 expression at mid-scotophase, whereas neither Clock nor Cry1 expression showed significant 24-h variations. This pattern was significantly disrupted (Clock, Bmal1) or changed in phase (Per1, Per2, Cry2) by CdCl(2) while melatonin counteracted the changes brought about by Cd on Per1 expression only. In animals receiving melatonin alone the 24-h pattern of MBH Per2 and Cry2 expression was disrupted. CdCl(2) disrupted the 24-h rhythmicity of Cu/Zn- and Mn-superoxide dismutase (SOD), nitric oxide synthase (NOS)-1, NOS-2, heme oxygenase (HO)-1, and HO-2 gene expression, most of the effects being counteracted by melatonin. In particular, the co-administration of melatonin and CdCl(2) increased Cu/Zn-SOD gene expression and decreased that of glutathione peroxidase (GPx), glutathione reductase (GSR), and HO-2. In animals receiving melatonin alone, significant increases in mean Cu/Zn and Mn-SOD gene expression, and decreases in that of GPx, GSR, NOS-1, NOS-2, HO-1, and HO-2, were found. The results indicate that the interfering effect of melatonin on the activity of a low dose of CdCl(2) on MBH clock and redox enzyme genes is mainly exerted at the level of redox enzyme gene expression.
Keywords: cadmium; circadian rhythms; clock genes; medial basal hypothalamus; melatonin; redox enzyme genes.
Figures

References
-
- Arendt J., Skene D. J. (2005). Melatonin as a chronobiotic. Sleep Med. Rev. 9, 25–39 - PubMed
-
- Artinian L. R., Ding J. M., Gillette M. U. (2001). Carbon monoxide and nitric oxide: interacting messengers in muscarinic signaling to the brain’s circadian clock. Exp. Neurol. 171, 293–300 - PubMed
-
- Beni S. M., Kohen R., Reiter R. J., Tan D. X., Shohami E. (2004). Melatonin-induced neuroprotection after closed head injury is associated with increased brain antioxidants and attenuated late-phase activation of NF-κB and AP-1. FASEB J. 18, 149–151 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

