Semi-Preparative Isolation and Purification of Three Tauro-Conjugated Cholic Acids from Pulvis Fellis Suis by HSCCC Coupled with ELSD Detection
- PMID: 21442029
- PMCID: PMC3063647
- DOI: 10.1007/s10337-010-1893-2
Semi-Preparative Isolation and Purification of Three Tauro-Conjugated Cholic Acids from Pulvis Fellis Suis by HSCCC Coupled with ELSD Detection
Abstract
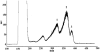
Coupled with evaporative light scattering detection, a high-speed counter-current chromatography (HSCCC) method was applied to the separation and purification of three tauro-conjugated cholic acids of taurochenodeoxycholic acid (TCDCA), taurohyodeoxycholic acid (THDCA) and taurohyocholic acid (THCA) from Pulvis Fellis Suis (Pig gallbladder bile) for the first time. The two-phase solvent system composed of chloroform-methanol-water-acetic acid (4:4:2:0.3, v/v/v/v) was selected for the one-step separation where the lower phase was used as the mobile phase in the head to tail elution mode. The revolution speed of the separation column, flow rate of the mobile phase and separation temperature were 800 rpm, 1.5 ml/min and 25°C respectively. From 100 mg of the crude extract, 10.2 mg of TCDCA, 11.8 mg of THDCA and 5.3 mg of THCA were obtained with the purity of 94.6%, 96.5% and 95.4%, respectively. in one step separation The HSCCC fractions were analyzed by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and the structures of the three tauro-conjugated cholic acids were identified by ESI-MS, (1)H NMR and (13)C NMR.
Figures
References
-
- Pharmacopoeia Committee, editor. Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China [M] Vol. 1. China Medical Science and Technology Publishing Co.; Beijing: 2010.
-
- Song LR. Dictionary of modern Chinese medicine. Vol. 2. People's Medical Publishing Co.; Beijing: 2001.
-
- Sun DN, Zou L. Contractile effects of cholic acid and bilirubin on umbilical arterial circle in vitro. Chin J Obs /Gyne & Pediatr (Electronic Edition) 2009;5:35–37.
-
- Zhang YJ, Luo QF, Zhang J. Efects of glycochenodeoxycholic acid on apoptosis of rat sinusoidal endothelial cells. Chin J Gastroenterology. 2006;11:281–285.
-
- Wang C, Li PF. Effect of taurocholic acid on cough and dyspnea. Anim Husbandry and Feed Sci. 2009;30:89–90.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources