Growth hormone enhances arachidonic acid metabolites in a growth hormone transgenic mouse
- PMID: 21442273
- PMCID: PMC4982394
- DOI: 10.1007/s11745-011-3548-y
Growth hormone enhances arachidonic acid metabolites in a growth hormone transgenic mouse
Abstract
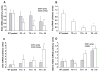
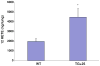
In a transgenic growth hormone (GH) mouse model, highly elevated GH increases overall growth and decreases adipose depots while low or moderate circulating GH enhances adipose deposition with differential effects on body growth. Using this model, the effects of low, moderate, and high chronic GH on fatty acid composition were determined for adipose and hepatic tissue and the metabolites of 20:4n-6 (arachidonic acid) were characterized to identify metabolic targets of action of elevated GH. The products of Δ-9 desaturase in hepatic, but not adipose, tissue were reduced in response to elevated GH. Proportional to the level of circulating GH, the products of Δ-5 and Δ-6 were increased in both adipose and hepatic tissue for the omega-6 lipids (e.g., 20:4n-6), while only the hepatic tissues showed an increase for omega-3 lipids (e.g., 22:6n-3). The eicosanoids, PGE₂ and 12-HETE, were elevated with high GH but circulating thromboxane was not. Hepatic PTGS1 and 2 (COX1 and COX 2), SOD1, and FADS2 (Δ-6 desaturase) mRNAs were increased with elevated GH while FAS mRNA was reduced; SCD1 (stearoyl-coenzyme A desaturase) and SCD2 mRNA did not significantly differ. The present study showed that GH influences the net flux through various aspects of lipid metabolism and especially the desaturase metabolic processes. The combination of altered metabolism and tissue specificity suggest that the regulation of membrane composition and its effects on signaling pathways, including the production and actions of eicosanoids, can be mediated by the GH regulatory axis.
Figures
References
-
- Nakamura MT, Nara TY. Structure, function, and dietary regulation of Δ6, Δ5, and Δ9 desaturases. Annu Rev Nutr. 2004;24:345–376. - PubMed
-
- Uauy R, Hoffman, Peirano P, et al. Essential fatty acids in visual and brain development. Lipids. 2001;36:685–695. - PubMed
-
- Kaiser E, Chiba P, Zaky K. Phospholipases in biology and medicine. Clin Biochem. 1990;23:349–370. - PubMed
-
- Makheja AN. Atherosclerosis: the eicosanoid connection. Mol Cell Biochem. 1992;111:137–142. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

