Elevated serum levels of heat shock protein 70 can be detected after radiofrequency ablation
- PMID: 21442384
- PMCID: PMC3156258
- DOI: 10.1007/s12192-011-0261-y
Elevated serum levels of heat shock protein 70 can be detected after radiofrequency ablation
Abstract
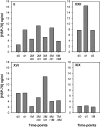
Due to their adjuvant effect and their ability to chaperone tumor-associated peptides, heat shock proteins constitute a potent alarm signal for the immune system and can lead to activation of anti-tumor T-cell immunity. Radiofrequency ablation has been reported to induce heat shock protein expression especially that of heat shock protein 70 in sublethally damaged tumor cells. In this study, we evaluated the release of heat shock protein 70 into the serum of cancer-bearing patients directly after radiofrequency ablation. Sera of 22 patients undergoing radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of primary and secondary malignancies of the liver, kidney, and lung, as well as control sera of 20 patients undergoing diagnostic liver biopsy were analyzed using a manufactured heat shock protein 70 ELISA. A significant increase in serum levels of heat shock protein 70 was detectable in the patient cohort 1 day after radiofrequency ablation. More than a twofold increase was observed in nine out of 22 patients, which tended to correlate with favorable clinical outcome. No patient of the control group revealed a comparable increase. Radiofrequency ablation can lead to a release of heat shock protein 70 into the serum, which is transiently detectable 1 day after treatment. Elevated heat shock protein 70 serum levels may constitute a biomarker for favorable clinical outcome.
Figures
References
-
- Abe M, Manola JB, Oh WK, Parslow DL, George DJ, Austin CL, Kantoff PW. Plasma levels of heat shock protein 70 in patients with prostate cancer: a potential biomarker for prostate cancer. Clin Prostate Cancer. 2004;3:49–53. - PubMed
-
- Blachere NE, Udono H, Janetzki S, Li Z, Heike M, Srivastava PK. Heat shock protein vaccines against cancer. J Immunother Emphasis Tumor Immunol. 1993;14:352–356. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources