S-nitrosylation of ApoE in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 21443265
- PMCID: PMC3082618
- DOI: 10.1021/bi200266v
S-nitrosylation of ApoE in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
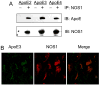
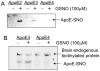
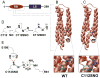
The mechanism by which apolipoprotein E (ApoE) isoforms functionally influence the risk and progression of late-onset Alzheimer's disease (LOAD) remains hitherto unknown. Herein, we present evidence that all ApoE isoforms bind to nitric oxide synthase 1 (NOS1) and that such protein-protein interaction results in S-nitrosylation of ApoE2 and ApoE3 but not ApoE4. Our structural analysis at the atomic level reveals that S-nitrosylation of ApoE2 and ApoE3 proteins may lead to conformational changes resulting in the loss of binding to low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptors. Collectively, our data suggest that S-nitrosylation of ApoE proteins may play an important role in regulating lipid metabolism and in the pathogenesis of LOAD.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The association−dissociation behavior of the ApoE proteins: kinetic and equilibrium studies.Biochemistry. 2010 Nov 9;49(44):9533-41. doi: 10.1021/bi101407m. Biochemistry. 2010. PMID: 20923231 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma ApoE4 Levels Are Lower than ApoE2 and ApoE3 Levels, and Not Associated with Plasma Aβ40/42 Ratio as a Biomarker of Amyloid-β Amyloidosis in Alzheimer's Disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2023;93(1):333-348. doi: 10.3233/JAD-220996. J Alzheimers Dis. 2023. PMID: 36970894
-
Interaction of nascent ApoE2, ApoE3, and ApoE4 isoforms expressed in mammalian cells with amyloid peptide beta (1-40). Relevance to Alzheimer's disease.Biochemistry. 1997 Aug 26;36(34):10571-80. doi: 10.1021/bi9626362. Biochemistry. 1997. PMID: 9265639
-
Apolipoprotein E and oxidative stress in brain with relevance to Alzheimer's disease.Neurobiol Dis. 2020 May;138:104795. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2020.104795. Epub 2020 Feb 6. Neurobiol Dis. 2020. PMID: 32036033 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apolipoprotein E: from cardiovascular disease to neurodegenerative disorders.J Mol Med (Berl). 2016 Jul;94(7):739-46. doi: 10.1007/s00109-016-1427-y. Epub 2016 Jun 9. J Mol Med (Berl). 2016. PMID: 27277824 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A systematic review of molecular approaches that link mitochondrial dysfunction and neuroinflammation in Parkinson's disease.Neurol Sci. 2021 Nov;42(11):4459-4469. doi: 10.1007/s10072-021-05551-1. Epub 2021 Sep 3. Neurol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34480241
-
Functional diversity of apolipoprotein E: from subcellular localization to mitochondrial function.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 Aug 26;79(9):499. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04516-7. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 36018414 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aberrant protein s-nitrosylation in neurodegenerative diseases.Neuron. 2013 May 22;78(4):596-614. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.05.005. Neuron. 2013. PMID: 23719160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detection of S-nitroso compounds by use of midinfrared cavity ring-down spectroscopy.Anal Chem. 2015 Mar 17;87(6):3345-53. doi: 10.1021/ac5045143. Epub 2015 Mar 3. Anal Chem. 2015. PMID: 25692741 Free PMC article.
-
S-nitrosylation: specificity, occupancy, and interaction with other post-translational modifications.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013 Oct 10;19(11):1209-19. doi: 10.1089/ars.2012.5056. Epub 2013 Jan 4. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013. PMID: 23157187 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Saunders AM, Strittmatter WJ, Schmechel D, George-Hyslop PH, Pericak-Vance MA, Joo SH, Rosi BL, Gusella JF, Crapper-MacLachlan DR, Alberts MJ, Hulette C, Crain B, Goldgaber D, Roses AD. Neurology. 1993;43:1467–1472. - PubMed
-
- Corder EH, Saunders AM, Strittmatter WJ, Schmechel DE, Gaskell PC, Small GW, Roses AD, Haines JL, Pericak-Vance MA. Science. 1993;512:921–923. - PubMed
-
- Bertram L, Lill CM, Tanzi RE. Neuron. 2010;68:270–281. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

