Susceptibility of the antioxidant selenoenyzmes thioredoxin reductase and glutathione peroxidase to alkylation-mediated inhibition by anticancer acylfulvenes
- PMID: 21443269
- PMCID: PMC3210965
- DOI: 10.1021/tx2000152
Susceptibility of the antioxidant selenoenyzmes thioredoxin reductase and glutathione peroxidase to alkylation-mediated inhibition by anticancer acylfulvenes
Abstract
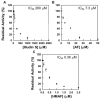
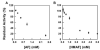
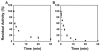
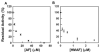
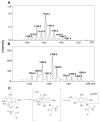
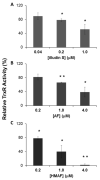
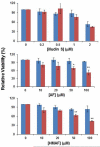
Selenium, in the form of selenocysteine, is a critical component of some major redox-regulating enzymes, including thioredoxin reductase (TrxR) and glutathione peroxidase (Gpx). TrxR has emerged as an anticancer target for drug development due to its elevated expression level in many aggressive human tumors. Acylfulvenes (AFs) are semisynthetic derivatives of the natural product illudin S and display improved cytotoxic selectivity profiles. AF and illudin S alkylate cellular macromolecules. Compared to AFs, illudin S more readily reacts with thiol-containing small molecules such as cysteine, glutathione, and cysteine-containing peptides. However, a previous study indicates that the reactivity of AFs and illudin S with glutathione reductase, a thiol-containing enzyme, is inversely correlated with the reactivity toward small molecule thiols. In this study, we investigate mechanistic aspects underlying the enzymatic and cellular effects of the AFs and illudin S on thioredoxin reductase. Both AF and HMAF were found to inhibit mammalian TrxR in the low- to submicromolar range, but illudin S was significantly less potent. TrxR inhibition by AFs was shown to be irreversible, concentration- and time-dependent, and mediated by alkylation of C-terminus active site Sec/Cys residues. In contrast, neither AFs nor illudin S inhibits Gpx, demonstrating that enzyme structure-specific small molecule interactions have a significant influence over the inherent reactivity of the Sec residue. In human cancer cells, TrxR activity can be inhibited by low micromolar concentrations of all three drugs. Finally, it was demonstrated that preconditioning cells by the addition of selenite to the cell culture media results in an enhancement in cell sensitivity toward AFs. These data suggest potential strategies for increasing drug activity by combination treatments that promote selenium enzyme activity.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Profiling patterns of glutathione reductase inhibition by the natural product illudin S and its acylfulvene analogues.Mol Biosyst. 2009 Sep;5(9):1013-24. doi: 10.1039/b904720d. Epub 2009 Jul 8. Mol Biosyst. 2009. PMID: 19668867 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical and enzymatic reductive activation of acylfulvene to isomeric cytotoxic reactive intermediates.Chem Res Toxicol. 2011 Nov 21;24(11):2044-54. doi: 10.1021/tx200401u. Epub 2011 Oct 14. Chem Res Toxicol. 2011. PMID: 21939268 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of both thioredoxin reductase and glutathione reductase may contribute to the anticancer mechanism of TH-302.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2010 Sep;136(3):294-301. doi: 10.1007/s12011-009-8544-1. Epub 2009 Oct 17. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2010. PMID: 19838642
-
Thioredoxin reductase inhibitors: a patent review.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2017 May;27(5):547-556. doi: 10.1080/13543776.2017.1272576. Epub 2016 Dec 26. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2017. PMID: 27977313 Review.
-
Recent advances in the development of thioredoxin reductase inhibitors as anticancer agents.Curr Drug Targets. 2012 Oct;13(11):1432-44. doi: 10.2174/138945012803530224. Curr Drug Targets. 2012. PMID: 22876886 Review.
Cited by
-
Irreversible TrxR1 inhibitors block STAT3 activity and induce cancer cell death.Sci Adv. 2020 Mar 20;6(12):eaax7945. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aax7945. eCollection 2020 Mar. Sci Adv. 2020. PMID: 32219156 Free PMC article.
-
The acylfulvene alkylating agent, LP-184, retains nanomolar potency in non-small cell lung cancer carrying otherwise therapy-refractory mutations.Oncotarget. 2021 Apr 13;12(8):791-806. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.27943. eCollection 2021 Apr 13. Oncotarget. 2021. PMID: 33889302 Free PMC article.
-
A Chemical Proteomic Analysis of Illudin-Interacting Proteins.Chemistry. 2019 Sep 25;25(54):12644-12651. doi: 10.1002/chem.201902919. Epub 2019 Sep 3. Chemistry. 2019. PMID: 31310394 Free PMC article.
-
Improved efficacy of acylfulvene in colon cancer cells when combined with a nuclear excision repair inhibitor.Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Nov 18;26(11):1674-82. doi: 10.1021/tx400255f. Epub 2013 Nov 5. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 24099590 Free PMC article.
-
Selenium compounds, apoptosis and other types of cell death: an overview for cancer therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(8):9649-9672. doi: 10.3390/ijms13089649. Epub 2012 Aug 2. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22949823 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Selenius M, Rundlöf A-K, Olm E, Fernandes AP, Björnstedt M. Selenium and the selenoprotein thioredoxin reductase in the prevention, treatment and diagnostics of cancer. Antioxid. Redox Signaling. 2010;12:867–880. - PubMed
-
- Rayman MP. Selenium in cancer prevention: a review of the evidence and mechanism of action. Proc. Nutr. Biochem. 2005;64:527–542. - PubMed
-
- Zeng H, Combs GF., Jr. Selenium as an anticancer nutrient: roles in cell proliferation and tumor cell invasion. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2008;19:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Sechi S, Chait BT. Modification of cysteine residues by alkylation. A tool in peptide mapping and protein identification. Anal. Chem. 1998;70:5150–5158. - PubMed
-
- Forstrom JW, Zakowski JJ, Tappel AL. Identification of the catalytic site of rat liver glutathione peroxidase as selenocysteine. Biochemistry. 1978;17:2639–2644. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

