Neuropharmacology of the naturally occurring kappa-opioid hallucinogen salvinorin A
- PMID: 21444610
- PMCID: PMC3082450
- DOI: 10.1124/pr.110.003244
Neuropharmacology of the naturally occurring kappa-opioid hallucinogen salvinorin A
Abstract
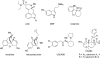
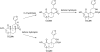
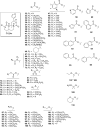
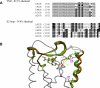
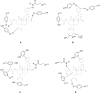
Salvia divinorum is a perennial sage native to Oaxaca, Mexico, that has been used traditionally in divination rituals and as a treatment for the "semimagical" disease panzón de borrego. Because of the intense "out-of-body" experiences reported after inhalation of the pyrolized smoke, S. divinorum has been gaining popularity as a recreational hallucinogen, and the United States and several other countries have regulated its use. Early studies isolated the neoclerodane diterpene salvinorin A as the principal psychoactive constituent responsible for these hallucinogenic effects. Since the finding that salvinorin A exerts its potent psychotropic actions through the activation of KOP receptors, there has been much interest in elucidating the underlying mechanisms behind its effects. These effects are particularly remarkable, because 1) salvinorin A is the first reported non-nitrogenous opioid receptor agonist, and 2) its effects are not mediated by the 5-HT(2A) receptor, the classic target of hallucinogens such as lysergic acid diethylamide and mescaline. Rigorous investigation into the structural features of salvinorin A responsible for opioid receptor affinity and selectivity has produced numerous receptor probes, affinity labels, and tools for evaluating the biological processes responsible for its observed psychological effects. Salvinorin A has therapeutic potential as a treatment for pain, mood and personality disorders, substance abuse, and gastrointestinal disturbances, and suggests that nonalkaloids are potential scaffolds for drug development for aminergic G-protein coupled receptors.
Figures

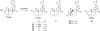


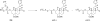
References
-
- Ansonoff MA, Zhang J, Czyzyk T, Rothman RB, Stewart J, Xu H, Zjwiony J, Siebert DJ, Yang F, Roth BL, et al. (2006) Antinociceptive and hypothermic effects of Salvinorin A are abolished in a novel strain of kappa-opioid receptor-1 knockout mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 318:641–648 - PubMed
-
- Babu KM, McCurdy CR, Boyer EW. (2008) Opioid receptors and legal highs: Salvia divinorum and Kratom. Clin Toxicol (Phila) 46:146–152 - PubMed
-
- Baggott MJ, Erowid E, Erowid F, Galloway GP, Mendelson J. (2010) Use patterns and self-reported effects of Salvia divinorum: An internet-based survey. Drug Alcohol Depend 111:250–256 - PubMed
-
- Baker LE, Panos JJ, Killinger BA, Peet MM, Bell LM, Haliw LA, Walker SL. (2009) Comparison of the discriminative stimulus effects of salvinorin A and its derivatives to U69,593 and U50,488 in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 203:203–211 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

