Pharmacokinetics and safety of MP-376 (levofloxacin inhalation solution) in cystic fibrosis subjects
- PMID: 21444699
- PMCID: PMC3101414
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01744-10
Pharmacokinetics and safety of MP-376 (levofloxacin inhalation solution) in cystic fibrosis subjects
Abstract
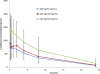
The pharmacokinetics and tolerability of nebulized MP-376 (levofloxacin inhalation solution [Aeroquin]) were determined in cystic fibrosis (CF) subjects. Ten CF subjects received single 180-mg doses of two formulations of MP-376, followed by a multiple-dose phase of 240 mg once daily for 7 days. Serum and expectorated-sputum samples were assayed for levofloxacin content. Safety was evaluated following the single- and multiple-dose study phases. Nebulized MP-376 produced high concentrations of levofloxacin in sputum. The mean maximum plasma concentration (C(max)) ranged between 2,563 and 2,932 mg/liter for 180-mg doses of the 50- and 100-mg/ml formulations, respectively. After 7 days of dosing, the mean C(max) for the 240-mg dose was 4,691 mg/liter. The mean serum levofloxacin C(max) ranged between 0.95 and 1.28 for the 180-mg doses and was 1.71 for the 240-mg dose. MP-376 was well tolerated. Nebulized MP-376 produces high sputum and low serum levofloxacin concentrations. The pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability were similar for the two formulations. MP-376 240 mg (100 mg/ml) is being advanced into late-stage clinical development.
Figures
References
-
- Ambrose P. G., et al. 2007. Pharmacokinetics-pharmacodynamics of antimicrobial therapy: it's not just for mice anymore. Clin. Infect. Dis. 44:79–86 - PubMed
-
- Conrad D., et al. 2010. Phase 2b study of inhaled MP-376 (Aeroquin, levofloxacin inhalation solution) in stable cystic fibrosis (CF) patients with chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PA) lung infection, abstr. A102. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 181(Meeting abstr.):A2339
-
- Geller D. E., et al. 2006. Pharmacokinetics of oral levofloxacin (LVX) in stable adult CF subjects. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 41(S29):328
-
- Geller D. E. 2008. The science of aerosol delivery in cystic fibrosis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 43(Suppl. 9):S5–S17
-
- Gibson R. L., Burns J. L., Ramsey B. W. 2003. Pathophysiology and management of pulmonary infections in cystic fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 168:918–951 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical