Mechanical signaling through the cytoskeleton regulates cell proliferation by coordinated focal adhesion and Rho GTPase signaling
- PMID: 21444750
- PMCID: PMC3065381
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.067009
Mechanical signaling through the cytoskeleton regulates cell proliferation by coordinated focal adhesion and Rho GTPase signaling
Abstract
The notion that cell shape and spreading can regulate cell proliferation has evolved over several years, but only recently has this been linked to forces from within and upon the cell. This emerging area of mechanical signaling is proving to be wide-spread and important for all cell types. The microenvironment that surrounds cells provides a complex spectrum of different, simultaneously active, biochemical, structural and mechanical stimuli. In this milieu, cells probe the stiffness of their microenvironment by pulling on the extracellular matrix (ECM) and/or adjacent cells. This process is dependent on transcellular cell-ECM or cell-cell adhesions, as well as cell contractility mediated by Rho GTPases, to provide a functional linkage through which forces are transmitted through the cytoskeleton by intracellular force-generating proteins. This Commentary covers recent advances in the underlying mechanisms that control cell proliferation by mechanical signaling, with an emphasis on the role of 3D microenvironments and in vivo extracellular matrices. Moreover, as there is much recent interest in the tumor-stromal interaction, we will pay particular attention to exciting new data describing the role of mechanical signaling in the progression of breast cancer.
Figures
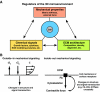


References
-
- Aijaz S., D'Atri F., Citi S., Balda M. S., Matter K. (2005). Binding of GEF-H1 to the tight junction-associated adaptor cingulin results in inhibition of Rho signaling and G1/S phase transition. Dev. Cell 8, 777-786 - PubMed
-
- Allinen M., Beroukhim R., Cai L., Brennan C., Lahti-Domenici J., Huang H., Porter D., Hu M., Chin L., Richardson A., et al. (2004). Molecular characterization of the tumor microenvironment in breast cancer. Cancer Cell 6, 17-32 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

