Histone demethylase JMJD2B functions as a co-factor of estrogen receptor in breast cancer proliferation and mammary gland development
- PMID: 21445275
- PMCID: PMC3060874
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017830
Histone demethylase JMJD2B functions as a co-factor of estrogen receptor in breast cancer proliferation and mammary gland development
Erratum in
-
Correction: Histone Demethylase JMJD2B Functions as a Co-Factor of Estrogen Receptor in Breast Cancer Proliferation and Mammary Gland Development.PLoS One. 2024 May 9;19(5):e0303780. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0303780. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38722939 Free PMC article.
Abstract
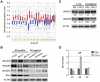
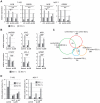
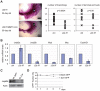
Estrogen is a key regulator of normal function of female reproductive system and plays a pivotal role in the development and progression of breast cancer. Here, we demonstrate that JMJD2B (also known as KDM4B) constitutes a key component of the estrogen signaling pathway. JMJD2B is expressed in a high proportion of human breast tumors, and that expression levels significantly correlate with estrogen receptor (ER) positivity. In addition, 17-beta-estradiol (E2) induces JMJD2B expression in an ERα dependent manner. JMJD2B interacts with ERα and components of the SWI/SNF-B chromatin remodeling complex. JMJD2B is recruited to ERα target sites, demethylates H3K9me3 and facilitates transcription of ER responsive genes including MYB, MYC and CCND1. As a consequence, knockdown of JMJD2B severely impairs estrogen-induced cell proliferation and the tumor formation capacity of breast cancer cells. Furthermore, Jmjd2b-deletion in mammary epithelial cells exhibits delayed mammary gland development in female mice. Taken together, these findings suggest an essential role for JMJD2B in the estrogen signaling, and identify JMJD2B as a potential therapeutic target in breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Jordan VC, O'Malley BW. Selective estrogen-receptor modulators and antihormonal resistance in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:5815–5824. - PubMed
-
- Robinson-Rechavi M, Escriva Garcia H, Laudet V. The nuclear receptor superfamily. J Cell Sci. 2003;116:585–586. - PubMed
-
- Brzozowski AM, Pike AC, Dauter Z, Hubbard RE, Bonn T, et al. Molecular basis of agonism and antagonism in the oestrogen receptor. Nature. 1997;389:753–758. - PubMed
-
- Rosenfeld MG, Lunyak VV, Glass CK. Sensors and signals: a coactivator/corepressor/epigenetic code for integrating signal-dependent programs of transcriptional response. Genes Dev. 2006;20:1405–1428. - PubMed
-
- Lonard DM, Lanz RB, O'Malley BW. Nuclear receptor coregulators and human disease. Endocr Rev. 2007;28:575–587. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

