Brahma is required for proper expression of the floral repressor FLC in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 21445315
- PMCID: PMC3061888
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017997
Brahma is required for proper expression of the floral repressor FLC in Arabidopsis
Abstract
Background: BRAHMA (BRM) is a member of a family of ATPases of the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complexes from Arabidopsis. BRM has been previously shown to be crucial for vegetative and reproductive development.
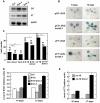
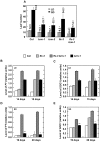
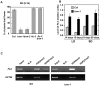
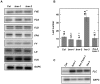
Methodology/principal findings: Here we carry out a detailed analysis of the flowering phenotype of brm mutant plants which reveals that, in addition to repressing the flowering promoting genes CONSTANS (CO), FLOWERING LOCUS T (FT) and SUPPRESSOR OF OVEREXPRESSION OF CO1 (SOC1), BRM also represses expression of the general flowering repressor FLOWERING LOCUS C (FLC). Thus, in brm mutant plants FLC expression is elevated, and FLC chromatin exhibits increased levels of histone H3 lysine 4 tri-methylation and decreased levels of H3 lysine 27 tri-methylation, indicating that BRM imposes a repressive chromatin configuration at the FLC locus. However, brm mutants display a normal vernalization response, indicating that BRM is not involved in vernalization-mediated FLC repression. Analysis of double mutants suggests that BRM is partially redundant with the autonomous pathway. Analysis of genetic interactions between BRM and the histone H2A.Z deposition machinery demonstrates that brm mutations overcome a requirement of H2A.Z for FLC activation suggesting that in the absence of BRM, a constitutively open chromatin conformation renders H2A.Z dispensable.
Conclusions/significance: BRM is critical for phase transition in Arabidopsis. Thus, BRM represses expression of the flowering promoting genes CO, FT and SOC1 and of the flowering repressor FLC. Our results indicate that BRM controls expression of FLC by creating a repressive chromatin configuration of the locus.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Floral regulators FLC and SOC1 directly regulate expression of the B3-type transcription factor TARGET OF FLC AND SVP 1 at the Arabidopsis shoot apex via antagonistic chromatin modifications.PLoS Genet. 2019 Apr 4;15(4):e1008065. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008065. eCollection 2019 Apr. PLoS Genet. 2019. PMID: 30946745 Free PMC article.
-
The chromatin remodelling ATPase BRAHMA interacts with GATA-family transcription factor GNC to regulate flowering time in Arabidopsis.J Exp Bot. 2022 Jan 27;73(3):835-847. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erab430. J Exp Bot. 2022. PMID: 34545936
-
The Arabidopsis Paf1c complex component CDC73 participates in the modification of FLOWERING LOCUS C chromatin.Plant Physiol. 2010 Jul;153(3):1074-84. doi: 10.1104/pp.110.158386. Epub 2010 May 12. Plant Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20463090 Free PMC article.
-
Control of the transition to flowering by chromatin modifications.Mol Plant. 2009 Jul;2(4):554-564. doi: 10.1093/mp/ssp005. Epub 2009 Mar 5. Mol Plant. 2009. PMID: 19825638 Review.
-
Recent advances in the chromatin-based mechanism of FLOWERING LOCUS C repression through autonomous pathway genes.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Aug 12;13:964931. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.964931. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36035698 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A SWI/SNF chromatin-remodeling complex acts in noncoding RNA-mediated transcriptional silencing.Mol Cell. 2013 Jan 24;49(2):298-309. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.11.011. Epub 2012 Dec 13. Mol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23246435 Free PMC article.
-
The Arabidopsis SWI2/SNF2 Chromatin Remodeling ATPase BRAHMA Targets Directly to PINs and Is Required for Root Stem Cell Niche Maintenance.Plant Cell. 2015 Jun;27(6):1670-80. doi: 10.1105/tpc.15.00091. Epub 2015 May 19. Plant Cell. 2015. PMID: 25991732 Free PMC article.
-
A SUMO Ligase AtMMS21 Regulates the Stability of the Chromatin Remodeler BRAHMA in Root Development.Plant Physiol. 2017 Mar;173(3):1574-1582. doi: 10.1104/pp.17.00014. Epub 2017 Jan 23. Plant Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28115583 Free PMC article.
-
The Chromatin-Remodeling Factor PICKLE Antagonizes Polycomb Repression of FT to Promote Flowering.Plant Physiol. 2019 Oct;181(2):656-668. doi: 10.1104/pp.19.00596. Epub 2019 Aug 3. Plant Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31377725 Free PMC article.
-
Gibberellin signaling modulates flowering via the DELLA-BRAHMA-NF-YC module in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell. 2023 Sep 1;35(9):3470-3484. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koad166. Plant Cell. 2023. PMID: 37294919 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Clapier CR, Cairns BR. The biology of chromatin remodeling complexes. Annu Rev Biochem. 2009;78:273–304. - PubMed
-
- Knizewski L, Ginalski K, Jerzmanowski A. Snf2 proteins in plants: gene silencing and beyond. Trends Plant Sci. 2008;13:557–565. - PubMed
-
- Kwon CS, Wagner D. Unwinding chromatin for development and growth: a few genes at a time. Trends Genet. 2007;23:403–412. - PubMed
-
- Farrona S, Hurtado L, Bowman JL, Reyes JC. The Arabidopsis thaliana SNF2 homolog AtBRM controls shoot development and flowering. Development. 2004;131:4965–4975. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

