Global array-based transcriptomics from minimal input RNA utilising an optimal RNA isolation process combined with SPIA cDNA probes
- PMID: 21445340
- PMCID: PMC3062544
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017625
Global array-based transcriptomics from minimal input RNA utilising an optimal RNA isolation process combined with SPIA cDNA probes
Abstract
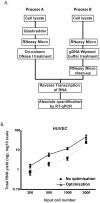
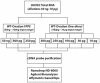
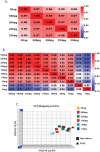
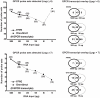
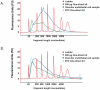
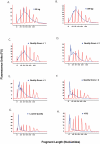
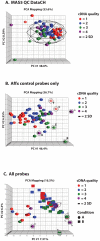
Technical advances in the collection of clinical material, such as laser capture microdissection and cell sorting, provide the advantage of yielding more refined and homogenous populations of cells. However, these attractive advantages are counter balanced by the significant difficulty in obtaining adequate nucleic acid yields to allow transcriptomic analyses. Established technologies are available to carry out global transcriptomics using nanograms of input RNA, however, many clinical samples of low cell content would be expected to yield RNA within the picogram range. To fully exploit these clinical samples the challenge of isolating adequate RNA yield directly and generating sufficient microarray probes for global transcriptional profiling from this low level RNA input has been addressed in the current report. We have established an optimised RNA isolation workflow specifically designed to yield maximal RNA from minimal cell numbers. This procedure obtained RNA yield sufficient for carrying out global transcriptional profiling from vascular endothelial cell biopsies, clinical material not previously amenable to global transcriptomic approaches. In addition, by assessing the performance of two linear isothermal probe generation methods at decreasing input levels of good quality RNA we demonstrated robust detection of a class of low abundance transcripts (GPCRs) at input levels within the picogram range, a lower level of RNA input (50 pg) than previously reported for global transcriptional profiling and report the ability to interrogate the transcriptome from only 10 pg of input RNA. By exploiting an optimal RNA isolation workflow specifically for samples of low cell content, and linear isothermal RNA amplification methods for low level RNA input we were able to perform global transcriptomics on valuable and potentially informative clinically derived vascular endothelial biopsies here for the first time. These workflows provide the ability to robustly exploit ever more common clinical samples yielding extremely low cell numbers and RNA yields for global transcriptomics.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Novel isothermal, linear nucleic acid amplification systems for highly multiplexed applications.Clin Chem. 2005 Oct;51(10):1973-81. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2005.053694. Epub 2005 Aug 25. Clin Chem. 2005. PMID: 16123149
-
Evaluation of methods for amplification of picogram amounts of total RNA for whole genome expression profiling.BMC Genomics. 2009 May 26;10:246. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-246. BMC Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19470167 Free PMC article.
-
Representation is faithfully preserved in global cDNA amplified exponentially from sub-picogram quantities of mRNA.Nat Biotechnol. 2002 Sep;20(9):940-3. doi: 10.1038/nbt729. Epub 2002 Aug 12. Nat Biotechnol. 2002. PMID: 12172558
-
Strategies for microarray analysis of limiting amounts of RNA.Brief Funct Genomic Proteomic. 2003 Apr;2(1):31-6. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/2.1.31. Brief Funct Genomic Proteomic. 2003. PMID: 15239941 Review.
-
cDNA amplification by SMART-PCR and suppression subtractive hybridization (SSH)-PCR.Methods Mol Biol. 2009;496:223-43. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-553-4_15. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 18839114 Review.
Cited by
-
A novel minimally-invasive method to sample human endothelial cells for molecular profiling.PLoS One. 2015 Feb 13;10(2):e0118081. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118081. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25679506 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Laser capture microdissection: Big data from small samples.Histol Histopathol. 2015 Nov;30(11):1255-69. doi: 10.14670/HH-11-622. Epub 2015 Apr 20. Histol Histopathol. 2015. PMID: 25892148 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chee M, Yang R, Hubbell E, Berno A, Huang XC, et al. Accessing genetic information with high-density DNA arrays. Science. 1996;274:610–614. - PubMed
-
- Pomeroy SL, Tamayo P, Gaasenbeek M, Sturla LM, Angelo M, et al. Prediction of central nervous system embryonal tumour outcome based on gene expression. Nature. 2002;415:436–442. - PubMed
-
- Cobleigh MA, Tabesh B, Bitterman P, Baker J, Cronin M, et al. Tumor gene expression and prognosis in breast cancer patients with 10 or more positive lymph nodes. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:8623–8631. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

