Cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation of pRb-like protein in root meristem cells of Vicia faba
- PMID: 21445688
- PMCID: PMC3249539
- DOI: 10.1007/s00709-011-0272-7
Cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation of pRb-like protein in root meristem cells of Vicia faba
Abstract
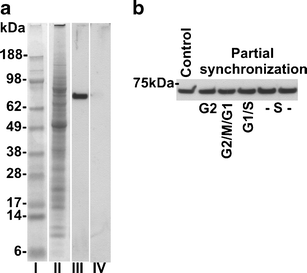
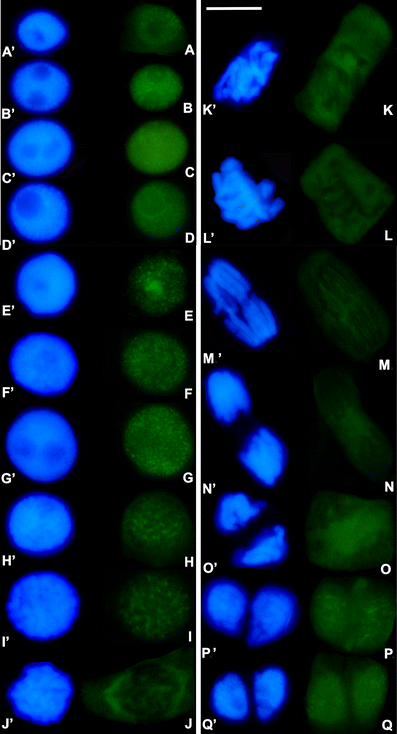
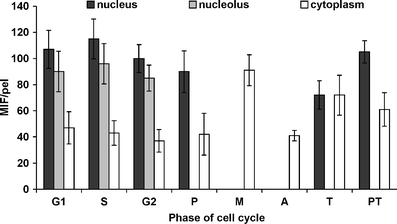
The retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein (pRb) regulates cell cycle progression by controlling the G1-to-S phase transition. As evidenced in mammals, pRb has three functionally distinct binding domains and interacts with a number of proteins including the E2F family of transcription factors, proteins with a conserved LxCxE motif (D-type cyclin), and c-Abl tyrosine kinase. CDK-mediated phosphorylation of pRb inhibits its ability to bind target proteins, thus enabling further progression of the cell cycle. As yet, the roles of pRb and pRb-binding factors have not been well characterized in plants. By using antibody which specifically recognizes phosphorylated serines (S807/811) in the c-Abl tyrosine kinase binding C-domain of human pRb, we provide evidence for the cell cycle-dependent changes in pRb-like proteins in root meristems cells of Vicia faba. An increased phosphorylation of this protein has been found correlated with the G1-to-S phase transition.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

