Characterization of HCV-specific CD4+Th17 immunity in recurrent hepatitis C-induced liver allograft fibrosis
- PMID: 21446979
- PMCID: PMC3076941
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2011.03458.x
Characterization of HCV-specific CD4+Th17 immunity in recurrent hepatitis C-induced liver allograft fibrosis
Abstract
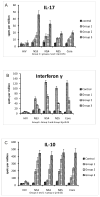
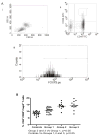
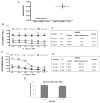
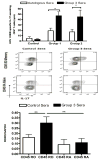
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) recurrence with accelerated fibrosis following orthotopic liver transplantation (OLT) is a universal phenomenon. To evaluate mechanisms contributing to HCV induced allograft fibrosis/cirrhosis, we investigated HCV-specific CD4+Th17 cells and their induction in OLT recipients with recurrence utilizing 51 HCV+ OLT recipients, 15 healthy controls and 9 HCV- OLT recipients. Frequency of HCV specific CD4+ Tcells secreting IFN-γ, IL-17 and IL-10 was analyzed by ELISpot. Serum cytokines and chemokines were analyzed by LUMINEX. Recipients with recurrent HCV induced allograft inflammation and fibrosis/cirrhosis demonstrated a significant increase in frequency of HCV specific CD4+Th17 cells. Increased pro-inflammatory mediators (IL-17, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8 and MCP-1), decreased IFN-γ, and increased IL-4, IL-5 and IL-10 levels were identified. OLT recipients with allograft inflammation and fibrosis/cirrhosis demonstrated increased frequency of Foxp3+ regulatory T cells (Tregs) that inhibited HCV specific CD4+Th1 but not Th17 cells. This suggests that recurrent HCV infection in OLT recipients induces an inflammatory milieu characterized by increased IL-6, IL-1β and decreased IFN-γ which facilitates induction of HCV specific CD4+Th17 cells. These cells are resistant to suppression by Tregs and may mediate an inflammatory cascade leading to cirrhosis in OLT recipients following HCV recurrence.
©2011 The Authors Journal compilation©2011 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons.
Figures


References
-
- Wright TL, Donegan E, Hsu HH, Ferrell L, Lake JR, Kim M, et al. Recurrent and acquired hepatitis C viral infection in liver transplant recipients. Gastroenterology. 1992;103(1):317–322. - PubMed
-
- Berenguer M, Lopez-Labrador FX, Wright TL. Hepatitis C and liver transplantation. J Hepatol. 2001;35(5):666–678. - PubMed
-
- Ferrari C, Valli A, Galati L, Penna A, Scaccaglia P, Giuberti T, et al. T-cell response to structural and nonstructural hepatitis C virus antigens in persistent and self-limited hepatitis C virus infections. Hepatology. 1994;19(2):286–295. - PubMed
-
- Sreenarasimhaiah J, Jaramillo A, Crippin J, Lisker-Melman M, Chapman WC, Mohanakumar T. Lack of optimal T-cell reactivity against the hepatitis C virus is associated with the development of fibrosis/cirrhosis during chronic hepatitis. Hum Immunol. 2003;64(2):224–230. - PubMed
-
- Chang KM, Thimme R, Melpolder JJ, Oldach D, Pemberton J, Moorhead-Loudis J, et al. Differential CD4(+) and CD8(+) T-cell responsiveness in hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatology. 2001;33(1):267–276. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

