A Bayesian model averaging approach for estimating the relative risk of mortality associated with heat waves in 105 U.S. cities
- PMID: 21447046
- PMCID: PMC3128186
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1541-0420.2011.01583.x
A Bayesian model averaging approach for estimating the relative risk of mortality associated with heat waves in 105 U.S. cities
Abstract
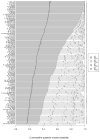
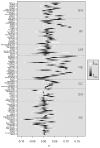
Estimating the risks heat waves pose to human health is a critical part of assessing the future impact of climate change. In this article, we propose a flexible class of time series models to estimate the relative risk of mortality associated with heat waves and conduct Bayesian model averaging (BMA) to account for the multiplicity of potential models. Applying these methods to data from 105 U.S. cities for the period 1987-2005, we identify those cities having a high posterior probability of increased mortality risk during heat waves, examine the heterogeneity of the posterior distributions of mortality risk across cities, assess sensitivity of the results to the selection of prior distributions, and compare our BMA results to a model selection approach. Our results show that no single model best predicts risk across the majority of cities, and that for some cities heat-wave risk estimation is sensitive to model choice. Although model averaging leads to posterior distributions with increased variance as compared to statistical inference conditional on a model obtained through model selection, we find that the posterior mean of heat wave mortality risk is robust to accounting for model uncertainty over a broad class of models.
© 2011, The International Biometric Society.
Figures

References
-
- Baccini M, Biggeri A, Accetta G, Kosatsky T, Katsouyanni K, Analitis A, Anderson HR, Bisanti L, D’Ippoliti D, Danova J, Forsberg B, Medina S, Paldy A, Rabczenko D, Schindler C, Michelozzi P. Heat effects on mortality in 15 European cities. Epidemiology. 2008;19(5):711–9. - PubMed
-
- Bai H, Islam MN, Kuroki H, Honda K, Wakasugi C. Deaths due to heat waves during the summer of 1994 in Osaka Prefecture, Japan. Nihon Hoigaku Zasshi. 1995;49(4):265–74. - PubMed
-
- Bailer AJ, Noble RB, Wheeler MW. Model uncertainty and risk estimation for experimental studies of quantal responses. Risk Anal. 2005;25(2):291–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

