Expression ratio of CCND1 to CDKN2A mRNA predicts RB1 status of cultured cancer cell lines and clinical tumor samples
- PMID: 21447152
- PMCID: PMC3072353
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-10-31
Expression ratio of CCND1 to CDKN2A mRNA predicts RB1 status of cultured cancer cell lines and clinical tumor samples
Abstract
Background: The retinoblastoma product (RB1) is frequently deregulated in various types of tumors by mutation, deletion, or inactivation through association with viral oncoproteins. The functional loss of RB1 is recognized to be one of the hallmarks that differentiate cancer cells from normal cells. Many researchers are attempting to develop anti-tumor agents that are preferentially effective against RB1-negative tumors. However, to identify patients with RB1-negative cancers, it is imperative to develop predictive biomarkers to classify RB1-positive and -negative tumors.
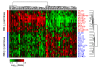
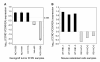
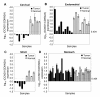
Results: Expression profiling of 30 cancer cell lines composed of 16 RB1-positive and 14 RB1-negative cancers was performed to find genes that are differentially expressed between the two groups, resulting in the identification of an RB1 signature with 194 genes. Among them, critical RB1 pathway components CDKN2A and CCND1 were included. We found that microarray data of the expression ratio of CCND1 and CDKN2A clearly distinguished the RB1 status of 30 cells lines. Measurement of the CCND1/CDKN2A mRNA expression ratio in additional cell lines by RT-PCR accurately predicted RB1 status (12/12 cells lines). The expression of CCND1/CDKN2A also correlated with RB1 status in xenograft tumors in vivo. Lastly, a CCND1/CDKN2A assay with clinical samples showed that uterine cervical and small cell lung cancers known to have a high prevalence of RB1-decifiency were predicted to be 100% RB1-negative, while uterine endometrial or gastric cancers were predicted to be 5-22% negative. All clinically normal tissues were 100% RB1-positive.
Conclusions: We report here that the CCND1/CDKN2A mRNA expression ratio predicts the RB1 status of cell lines in vitro and xenograft tumors and clinical tumor samples in vivo. Given the high predictive accuracy and quantitative nature of the CCND1/CDKN2A expression assay, the assay could be utilized to stratify patients for anti-tumor agents with preferential effects on either RB1-positive or -negative tumors.
Figures

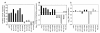
Similar articles
-
Molecular analysis of the Ink4a/Rb1-Arf/Tp53 pathways in radon-induced rat lung tumors.Lung Cancer. 2009 Mar;63(3):348-53. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2008.06.007. Epub 2008 Jul 25. Lung Cancer. 2009. PMID: 18656278
-
p16-Cdk4-Rb axis controls sensitivity to a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor PD0332991 in glioblastoma xenograft cells.Neuro Oncol. 2012 Jul;14(7):870-81. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nos114. Epub 2012 Jun 18. Neuro Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22711607 Free PMC article.
-
Heterogeneous abnormalities of CCND1 and RB1 in primary cutaneous T-Cell lymphomas suggesting impaired cell cycle control in disease pathogenesis.J Invest Dermatol. 2006 Jun;126(6):1388-95. doi: 10.1038/sj.jid.5700224. J Invest Dermatol. 2006. PMID: 16614728
-
Virtually 100% of melanoma cell lines harbor alterations at the DNA level within CDKN2A, CDKN2B, or one of their downstream targets.Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1998 Jun;22(2):157-63. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1098-2264(199806)22:2<157::aid-gcc11>3.0.co;2-n. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1998. PMID: 9598804 Review.
-
Tissue microarray profiling of cancer specimens and cell lines: opportunities and limitations.Lab Invest. 2001 Oct;81(10):1331-8. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.3780347. Lab Invest. 2001. PMID: 11598146 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression Analysis of Genes Involved in the RB/E2F Pathway in Astrocytic Tumors.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 28;10(8):e0137259. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137259. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26317630 Free PMC article.
-
Novel RB1-Loss Transcriptomic Signature Is Associated with Poor Clinical Outcomes across Cancer Types.Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Jul 15;25(14):4290-4299. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-0404. Epub 2019 Apr 22. Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31010837 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of signalling pathways activated by Tyro3 that promote cell survival, proliferation and invasiveness in human cancer cells.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2021 Aug 23;28:101111. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2021.101111. eCollection 2021 Dec. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2021. PMID: 34471705 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Oncogenomic Profiling of Copy Numbers and Gene Expression in Lung Adenocarcinomas without EGFR Mutations or ALK Fusion.J Cancer. 2018 Feb 28;9(6):1096-1105. doi: 10.7150/jca.23909. eCollection 2018. J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29581789 Free PMC article.
-
Depleting ANTXR1 suppresses glioma growth via deactivating PI3K/AKT pathway.Cell Cycle. 2023 Oct;22(19):2097-2112. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2023.2275900. Epub 2023 Dec 5. Cell Cycle. 2023. PMID: 37974357 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hernando E, Nahlé Z, Juan G, Diaz-Rodriguez E, Alaminos M, Hemann M, Michel L, Mittal V, Gerald W, Benezra R, Lowe SW, Cordon-Cardo C. Rb inactivation promotes genomic instability by uncoupling cell cycle progression from mitotic control. Nature. 2004;430:797–802. doi: 10.1038/nature02820. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

