The highly accurate anteriolateral portal for injecting the knee
- PMID: 21447197
- PMCID: PMC3077322
- DOI: 10.1186/1758-2555-3-6
The highly accurate anteriolateral portal for injecting the knee
Abstract
Background: The extended knee lateral midpatellar portal for intraarticular injection of the knee is accurate but is not practical for all patients. We hypothesized that a modified anteriolateral portal where the synovial membrane of the medial femoral condyle is the target would be highly accurate and effective for intraarticular injection of the knee.
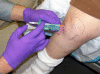
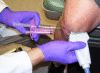
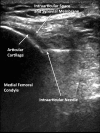
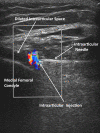
Methods: 83 subjects with non-effusive osteoarthritis of the knee were randomized to intraarticular injection using the modified anteriolateral bent knee versus the standard lateral midpatellar portal. After hydrodissection of the synovial membrane with lidocaine using a mechanical syringe (reciprocating procedure device), 80 mg of triamcinolone acetonide were injected into the knee with a 2.0-in (5.1-cm) 21-gauge needle. Baseline pain, procedural pain, and pain at outcome (2 weeks and 6 months) were determined with the 10 cm Visual Analogue Pain Score (VAS). The accuracy of needle placement was determined by sonographic imaging.
Results: The lateral midpatellar and anteriolateral portals resulted in equivalent clinical outcomes including procedural pain (VAS midpatellar: 4.6 ± 3.1 cm; anteriolateral: 4.8 ± 3.2 cm; p = 0.77), pain at outcome (VAS midpatellar: 2.6 ± 2.8 cm; anteriolateral: 1.7 ± 2.3 cm; p = 0.11), responders (midpatellar: 45%; anteriolateral: 56%; p = 0.33), duration of therapeutic effect (midpatellar: 3.9 ± 2.4 months; anteriolateral: 4.1 ± 2.2 months; p = 0.69), and time to next procedure (midpatellar: 7.3 ± 3.3 months; anteriolateral: 7.7 ± 3.7 months; p = 0.71). The anteriolateral portal was 97% accurate by real-time ultrasound imaging.
Conclusion: The modified anteriolateral bent knee portal is an effective, accurate, and equivalent alternative to the standard lateral midpatellar portal for intraarticular injection of the knee.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT00651625.
Figures



References
-
- Altman RD, Moskowitz R. Intraarticular sodium hyaluronate (Hyalgan) in the treatment of patients with osteoarthritis of the knee: a trial. Hyalgan Study Group. J Rheumatol. 1998;25:2203–12. - PubMed
-
- Jackson DW, Evans NA, Thomas BM. Accuracy of needle placement into the intra-articular space of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84-A(9):1522–1527. - PubMed
-
- Jackson DW, Simon TM, Aberman HM. Symptomatic articular cartilage degeneration: the impact in the new millennium. Clin Orthop. 2001;391(Suppl):S14–25. - PubMed
-
- Leopold SS, Redd BB, Warme WJ, Wehrle PA, Pettis PD, Shott S. Corticosteroid compared with hyaluronic acid injections for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee. A prospective, randomized trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85-A:1197–203. - PubMed
-
- Lussier A, Cividino AA, McFarlane CA, Olszynski WP, Potashner WJ, De Medicis R. Viscosupplementation with hylan for the treatment of osteoarthritis: findings from clinical practice in Canada. J Rheumatol. 1996;23:1579–85. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

