Spontaneously diabetic Ins2(+/Akita):apoE-deficient mice exhibit exaggerated hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis
- PMID: 21447785
- PMCID: PMC3129838
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00034.2011
Spontaneously diabetic Ins2(+/Akita):apoE-deficient mice exhibit exaggerated hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis
Abstract
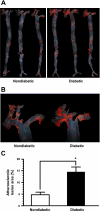
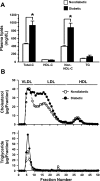
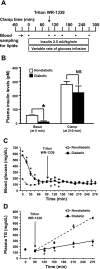
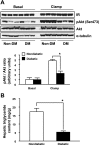
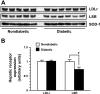
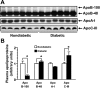
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) increases the risk of adverse coronary events. Among risk factors, dyslipidemia due to altered hepatic lipoprotein metabolism plays a central role in diabetic atherosclerosis. Nevertheless, the likely alterations in plasma lipid/lipoprotein profile remain unclear, especially in the context of spontaneously developed T1D and atherosclerosis. To address this question, we generated Ins2(+/Akita):apoE(-/-) mouse by cross-breeding Ins2(+/Akita) mouse (which has Ins2 gene mutation, causing pancreatic β-cell apoptosis and insulin deficiency) with apoE(-/-) mouse. Ins2(+/Akita):apoE(-/-) mice developed T1D spontaneously at 4-5 wk of age. At 25 wk of age and while on a standard chow diet, diabetic Ins2(+/Akita):apoE(-/-) mice exhibited an approximately threefold increase in atherosclerotic plaque in association with an approximatelty twofold increase in plasma non-HDL cholesterol, predominantly in the LDL fraction, compared with nondiabetic controls. To determine factors contributing to the exaggerated hypercholesterolemia, we assessed hepatic VLDL secretion and triglyceride content, expression of hepatic lipoprotein receptors, and plasma apolipoprotein composition. Diabetic Ins2(+/Akita):apoE(-/-) mice exhibited diminished VLDL secretion by ~50%, which was accompanied by blunted Akt phosphorylation in response to insulin infusion and decreased triglyceride content in the liver. Although the expression of hepatic LDL receptor was not affected, there was a significant reduction in the expression of lipolysis-stimulated lipoprotein receptor (LSR) by ~28%. Moreover, there was a marked decrease in plasma apoB-100 with a significant increase in apoB-48 and apoC-III levels. In conclusion, exaggerated hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis in spontaneously diabetic Ins2(+/Akita):apoE(-/-) mice may be attributable to impaired lipoprotein clearance in the setting of diminished expression of LSR and altered apolipoprotein composition of lipoproteins.
Figures
References
-
- Albers JJ, Marcovina SM, Imperatore G, Snively BM, Stafford J, Fujimoto WY, Mayer-Davis EJ, Petitti DB, Pihoker C, Dolan L, Dabelea DM. Prevalence and determinants of elevated apolipoprotein B and dense low-density lipoprotein in youths with type 1 and type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93: 735–742, 2008 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barber AJ, Antonetti DA, Kern TS, Reiter CE, Soans RS, Krady JK, Levison SW, Gardner TW, Bronson SK. The Ins2Akita mouse as a model of early retinal complications in diabetes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 46: 2210–2218, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Biddinger SB, Hernandez-Ono A, Rask-Madsen C, Haas JT, Aleman JO, Suzuki R, Scapa EF, Agarwal C, Carey MC, Stephanopoulos G, Cohen DE, King GL, Ginsberg HN, Kahn CR. Hepatic insulin resistance is sufficient to produce dyslipidemia and susceptibility to atherosclerosis. Cell Metab 7: 125–134, 2008 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

