T-cell receptor-induced JNK activation requires proteolytic inactivation of CYLD by MALT1
- PMID: 21448133
- PMCID: PMC3101995
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2011.85
T-cell receptor-induced JNK activation requires proteolytic inactivation of CYLD by MALT1
Abstract
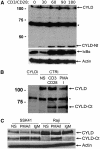
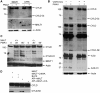
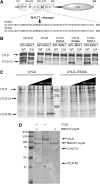
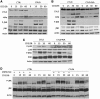
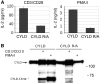
The paracaspase mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue 1 (MALT1) is central to lymphocyte activation and lymphomagenesis. MALT1 mediates antigen receptor signalling to NF-κB by acting as a scaffold protein. Furthermore, MALT1 has proteolytic activity that contributes to optimal NF-κB activation by cleaving the NF-κB inhibitor A20. Whether MALT1 protease activity is involved in other signalling pathways, and the identity of the relevant substrates, is unknown. Here, we show that T-cell receptors (TCR) activation, as well as overexpression of the oncogenic API2-MALT1 fusion protein, results in proteolytic inactivation of CYLD by MALT1, which is specifically required for c-jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) activation and the inducible expression of a subset of genes. These results indicate a novel role for MALT1 proteolytic activity in TCR-induced JNK activation and reveal CYLD cleavage as the underlying mechanism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
T cell antigen receptor stimulation induces MALT1 paracaspase-mediated cleavage of the NF-kappaB inhibitor A20.Nat Immunol. 2008 Mar;9(3):263-71. doi: 10.1038/ni1561. Epub 2008 Jan 27. Nat Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18223652
-
MALT1-dependent cleavage of CYLD promotes NF-κB signaling and growth of aggressive B-cell receptor-dependent lymphomas.Blood Cancer J. 2023 Mar 15;13(1):37. doi: 10.1038/s41408-023-00809-7. Blood Cancer J. 2023. PMID: 36922488 Free PMC article.
-
Protein kinase C-δ negatively regulates T cell receptor-induced NF-κB activation by inhibiting the assembly of CARMA1 signalosome.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jun 8;287(24):20081-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.335463. Epub 2012 Apr 23. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22528498 Free PMC article.
-
MALT1 substrate cleavage: what is it good for?Front Immunol. 2024 May 28;15:1412347. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1412347. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38863711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MALT1--a universal soldier: multiple strategies to ensure NF-κB activation and target gene expression.FEBS J. 2015 Sep;282(17):3286-97. doi: 10.1111/febs.13325. Epub 2015 Jun 10. FEBS J. 2015. PMID: 25996250 Review.
Cited by
-
The HECTD3 E3 ubiquitin ligase suppresses cisplatin-induced apoptosis via stabilizing MALT1.Neoplasia. 2013 Jan;15(1):39-48. doi: 10.1593/neo.121362. Neoplasia. 2013. PMID: 23358872 Free PMC article.
-
MALT1 Proteolytic Activity Suppresses Autoimmunity in a T Cell Intrinsic Manner.Front Immunol. 2019 Aug 14;10:1898. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01898. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31474984 Free PMC article.
-
The paracaspase MALT1 cleaves HOIL1 reducing linear ubiquitination by LUBAC to dampen lymphocyte NF-κB signalling.Nat Commun. 2015 Nov 3;6:8777. doi: 10.1038/ncomms9777. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 26525107 Free PMC article.
-
Erasing marks: Functions of plant deubiquitylating enzymes in modulating the ubiquitin code.Plant Cell. 2024 Sep 3;36(9):3057-3073. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koae129. Plant Cell. 2024. PMID: 38656977 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The protease activity of the paracaspase MALT1 is controlled by monoubiquitination.Nat Immunol. 2013 Apr;14(4):337-45. doi: 10.1038/ni.2540. Epub 2013 Feb 17. Nat Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23416615
References
-
- Angel P, Hattori K, Smeal T, Karin M (1988) The jun proto-oncogene is positively autoregulated by its product, Jun/AP-1. Cell 55: 875–885 - PubMed
-
- Coornaert B, Baens M, Heyninck K, Bekaert T, Haegman M, Staal J, Sun L, Chen ZJ, Marynen P, Beyaert R (2008) T cell antigen receptor stimulation induces MALT1 paracaspase-mediated cleavage of the NF-κB inhibitor A20. Nat Immunol 9: 263–271 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

