Characterization of human erythrocytes as potential carrier for pravastatin: an in vitro study
- PMID: 21448309
- PMCID: PMC3065791
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.8.222
Characterization of human erythrocytes as potential carrier for pravastatin: an in vitro study
Abstract
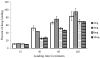
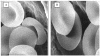
Drug delivery systems including chemical, physical and biological agents that enhance the bioavailability, improve pharmacokinetics and reduce toxicities of the drugs. Carrier erythrocytes are one of the most promising biological drug delivery systems investigated in recent decades. The bioavailability of statin drugs is low due the effects of P-glycoprotein in the gastro-intestinal tract as well as the first-pass metabolism. Therefore in this work we study the effect of time, temperature as well as concentration on the loading of pravastatin in human erythrocytes to be using them as systemic sustained release delivery system for this drug. After the loading process is performed the carriers' erythrocytes were physically and cellulary characterized. Also, the in vitro release of pravastatin from carrier erythrocytes was studied over time interval. Our results revealed that, human erythrocytes have been successfully loaded with pravastatin using endocytosis method either at 25(o)C or at 37(o)C. The loaded amount at 10 mg/ml is 0.32 mg/0.1 ml and 0.69 mg/0.1 ml. Entrapment efficiency is 34% and 94% at 25(o)C and 37(o)C respectively at drug concentration 4 mg/ml. Moreover the percent of cells recovery is 87-93%. Hematological parameters and osmotic fragility behavior of pravastatin loaded erythrocytes were similar that of native erythrocytes. Scanning electron microscopy demonstrated that the pravastatin loaded cells has no change in the morphology. Pravastatin releasing from carrier cell was 83% after 23 hours in phosphate buffer saline and decreased to 72% by treatment of carrier cells with glutaraldehyde. The releasing pattern of the drug from loaded erythrocytes obeyed first order kinetics. It concluded that pravastatin is successfully entrapped into erythrocytes with acceptable loading parameters and moderate morphological changes, this suggesting that erythrocytes can be used as prolonged release for pravastatin.
Keywords: drug delivery; erythrocytes; osmotic fragility; pravastatin.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Erythrocyte-mediated delivery of pravastatin: in vitro study of effect of hypotonic lysis on biochemical parameters and loading efficiency.Arch Pharm Res. 2012 Aug;35(8):1431-9. doi: 10.1007/s12272-012-0813-4. Epub 2012 Sep 1. Arch Pharm Res. 2012. PMID: 22941486
-
Preparation and in vitro evaluation of carrier erythrocytes for RES-targeted delivery of interferon-alpha 2b.Int J Pharm. 2007 Aug 16;341(1-2):125-33. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2007.04.001. Epub 2007 Apr 6. Int J Pharm. 2007. PMID: 17512685
-
Preparation and in-vitro characterization of tramadol-loaded carrier erythrocytes for long-term intravenous delivery.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2011 Mar;63(3):322-32. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.2010.01207.x. Epub 2010 Dec 22. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21749379
-
Carrier erythrocytes: an overview.Drug Deliv. 2003 Jan-Mar;10(1):9-20. doi: 10.1080/713840329. Drug Deliv. 2003. PMID: 12554359 Review.
-
Drug loaded erythrocytes: as novel drug delivery system.Curr Pharm Des. 2008;14(1):63-70. doi: 10.2174/138161208783330772. Curr Pharm Des. 2008. PMID: 18220819 Review.
Cited by
-
Drug-loaded erythrocytes: on the road toward marketing approval.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016 Feb 11;10:665-76. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S96470. eCollection 2016. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016. PMID: 26929599 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Erythrocytes as Carriers: From Drug Delivery to Biosensors.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Mar 18;12(3):276. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12030276. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 32197542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intelligent berberine-loaded erythrocytes attenuated inflammatory cytokine productions in macrophages.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 23;14(1):9381. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-60103-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38654085 Free PMC article.
-
Red blood cells: a potential delivery system.J Nanobiotechnology. 2023 Aug 22;21(1):288. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-02060-5. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023. PMID: 37608283 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The discovery of berberine erythrocyte-hemoglobin self-assembly delivery system: a neglected carrier underlying its pharmacokinetics.Drug Deliv. 2022 Dec;29(1):856-870. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2022.2036870. Drug Deliv. 2022. PMID: 35277093 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McFarlane SI, Muniyappa R, Francisco R, Sowers JR. Clinical review 145: Pleiotropic effects of statins: lipid reduction and beyond. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87(4):1451–1458. - PubMed
-
- Moghadasian MH. Clinical pharmacology of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme a reductase inhibitors. Life Sciences. 1999;65(13):1329–1337. - PubMed
-
- Williams D, Feely J. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic drug interactions with HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2002;41(5):343–370. - PubMed
-
- Hatanaka T. Clinical pharmacokinetics of pravastatin: mechanisms of pharmacokinetic events. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2000;39:397–412. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

