Promising effect of infliximab on the extent of involvement in ulcerative colitis
- PMID: 21448377
- PMCID: PMC3063437
Promising effect of infliximab on the extent of involvement in ulcerative colitis
Abstract
Background: Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a disabling disease with increasing incidence in Iran. In spite of combined medical therapy, some patients eventually undergo total colectomy. Infliximab has proved itself as a rescue therapy and even as an early aggressive therapy for severe extensive UC. Meantime, there are concerns about its complications. The aim of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of infliximab in Iranian refractory UC patients.
Methods: This multi centric case-series study included 29 UC patients receiving two to three of the drugs prednisolone, AZT/6MP and 5ASA but yet having flare-ups. At first, the extent of colon involvement was determined by colonoscopy; then the drug was administered at baseline, 2nd week and 6th week and colonoscopy repeated afterwards. Clinical and laboratory data were also recorded.
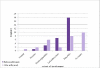
Results: In first endoscopy 18 patients (62%) out of 29 suffered from pancolitis and none had normal results. In second examination (done on 19 patients), one was normal and only 8 of 18 (27.6%) had pancolitis. Considering missing cases, at least in 33.3% of patients the drug has reduced the extreme extent of colon involvement. Also a wilcoxon signed ranks test revealed significant reduction of the disease extension after this treatment (p = 0.008). There were only one leucopenic and one hypotensive reactions in short term. The drug showed effectiveness in the term of disease modifying, too.
Conclusions: These data show the usefulness of the drug in refractory UC. Longer follow ups and controlled trials are needed.
Keywords: Colitis; Colon; Infliximab; Ulcerative.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Generalized Pyoderma Gangrenosum Associated with Ulcerative Colitis: Successful Treatment with Infliximab and Azathioprine.Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2016 Apr;24(1):83-5. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2016. PMID: 27149138
-
A review of infliximab use in ulcerative colitis.Clin Ther. 2008 Feb;30(2):223-30. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2008.02.014. Clin Ther. 2008. PMID: 18343261 Review.
-
Induction and maintenance infliximab therapy in children with moderate to severe ulcerative colitis: Retrospective, multicenter study.Adv Clin Exp Med. 2017 Jan-Feb;26(1):57-61. doi: 10.17219/acem/42197. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2017. PMID: 28397433
-
Histological healing after infliximab induction therapy in children with ulcerative colitis.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Oct 7;21(37):10654-61. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i37.10654. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26457025 Free PMC article.
-
Infliximab and ulcerative colitis.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2006 Apr;6(4):401-8. doi: 10.1517/14712598.6.4.401. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2006. PMID: 16548766 Review.
References
-
- Grover P, Kamat D. Management of inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Pediatr. 2007;46(4):359–64. - PubMed
-
- Karlinger K, Györke T, Makö E, Mester A, Tarján Z. The epidemiology and the pathogenesis of inflammatory bo-wel disease. Eur J Radiol. 2000;35(3):154–67. - PubMed
-
- Wilhelm SM, McKenney KA, Rivait KN, Kale-Pradhan PB. A Review of infliximab use in ulcerative colitis. Clin Ther. 2008;30(2):223–30. - PubMed
-
- Aberra FN, Lichtenstein GR. Infliximab in ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2006;35(4):821–36. - PubMed
-
- Langan RC, Gotsch PB, Krafczyk MA, Skillinge DD. Ulcerative colitis: diagnosis and treatment. Am Fam Physician. 2007;76(9):1323–30. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources