Interleukin-24 is correlated with differentiation and lymph node numbers in rectal cancer
- PMID: 21448421
- PMCID: PMC3063909
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i9.1167
Interleukin-24 is correlated with differentiation and lymph node numbers in rectal cancer
Abstract
Aim: To assess the significance of interleukin (IL)-24 and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression in lymph-node-positive rectal cancer.
Methods: Between 1998 and 2005, 90 rectal adenocarcinoma patients with lymph node involvement were enrolled. All patients received radical surgery and postoperative pelvic chemoradiotherapy of 50.4-54.0 Gy. Chemotherapy of 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin or levamisole was given intravenously during the first and last week of radiotherapy, and then monthly for about 6 mo. Expression of IL-24 and VEGF was evaluated by immunohistochemical staining of surgical specimens, and their relations with patient characteristics and survival were analyzed. The median follow-up of surviving patients was 73 mo (range: 52-122 mo).
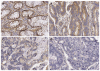
Results: IL-24 expression was found in 81 out of 90 patients; 31 showed weak intensity and 50 showed strong intensity. VEGF expression was found in 64 out of 90 patients. Negative and weak intensities of IL-24 expression were classified as negative expression for analysis. IL-24 expression was significantly reduced in poorly differentiated tumors in comparison with well or moderately differentiated tumors (P = 0.004), N2b to earlier N stages (P = 0.016), and stage IIIc to stage IIIa or IIIb (P = 0.028). The number of involved lymph nodes was also significantly reduced in IL-24-positive patients in comparison with IL-24-negative ones.There was no correlation between VEGF expression and patient characteristics. Expression of IL-24 and VEGF was not correlated with survival, but N stage and stages were significantly correlated with survival.
Conclusion: IL-24 expression was significantly correlated with histological differentiation, and inversely correlated with the degree of lymph node involvement in stage III rectal cancer.
Keywords: Histological differentiation; Interleukin-24; Lymph node; Rectal cancer; Vascular endothelial growth factor.
Figures
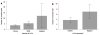
Similar articles
-
The reliability of lymph-node staging in rectal cancer after preoperative chemoradiotherapy.Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2005 Sep;17(6):448-55. doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2005.05.007. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2005. PMID: 16149289
-
lymph node ratio as a prognostic factor in patients with stage III rectal cancer treated with total mesorectal excision followed by chemoradiotherapy.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009 Jul 1;74(3):796-802. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.08.065. Epub 2009 Mar 14. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009. PMID: 19289261
-
Metastatic lymph node ratio in stage III rectal carcinoma is a valuable prognostic factor even with less than 12 lymph nodes retrieved: a prospective study.Am J Surg. 2014 Jun;207(6):824-31. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2013.07.022. Epub 2013 Oct 8. Am J Surg. 2014. PMID: 24112666
-
Gene expression profiles of epidermal growth factor receptor, vascular endothelial growth factor and hypoxia-inducible factor-1 with special reference to local responsiveness to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy and disease recurrence after rectal cancer surgery.Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2010 May;22(4):272-80. doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2010.01.001. Epub 2010 Feb 1. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2010. PMID: 20117921
-
Successful resection of metachronous para-aortic, Virchow lymph node and liver metastatic recurrence of rectal cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Nov 28;21(44):12722-8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i44.12722. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26640350 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Gene expression profiling of the leading edge of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: IL-24-driven MMP-7.J Invest Dermatol. 2014 May;134(5):1418-1427. doi: 10.1038/jid.2013.494. Epub 2013 Nov 22. J Invest Dermatol. 2014. PMID: 24270662 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-24 Regulates T Cell Activity in Patients With Colorectal Adenocarcinoma.Front Oncol. 2019 Dec 10;9:1401. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01401. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31921658 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of lymph node metastasis in patients with T1-stage colorectal cancer from multiple centers in China.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 Dec 28;23(48):8582-8590. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i48.8582. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 29358866 Free PMC article.
-
IL-20 Subfamily Biological Effects: Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Perspectives in Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 29;26(15):7320. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157320. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806452 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ILs-3, 6 and 11 increase, but ILs-10 and 24 decrease stemness of human prostate cancer cells in vitro.Oncotarget. 2015 Dec 15;6(40):42687-703. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5883. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26528857 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smalley SR, Benedetti JK, Williamson SK, Robertson JM, Estes NC, Maher T, Fisher B, Rich TA, Martenson JA, Kugler JW, et al. Phase III trial of fluorouracil-based chemotherapy regimens plus radiotherapy in postoperative adjuvant rectal cancer: GI INT 0144. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:3542–3547. - PubMed
-
- Jiang H, Lin JJ, Su ZZ, Goldstein NI, Fisher PB. Subtraction hybridization identifies a novel melanoma differentiation associated gene, mda-7, modulated during human melanoma differentiation, growth and progression. Oncogene. 1995;11:2477–2486. - PubMed
-
- Ellerhorst JA, Prieto VG, Ekmekcioglu S, Broemeling L, Yekell S, Chada S, Grimm EA. Loss of MDA-7 expression with progression of melanoma. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:1069–1074. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

