T(1) independent, T(2) (*) corrected chemical shift based fat-water separation with multi-peak fat spectral modeling is an accurate and precise measure of hepatic steatosis
- PMID: 21448952
- PMCID: PMC3130738
- DOI: 10.1002/jmri.22514
T(1) independent, T(2) (*) corrected chemical shift based fat-water separation with multi-peak fat spectral modeling is an accurate and precise measure of hepatic steatosis
Abstract
Purpose: To determine the precision and accuracy of hepatic fat-fraction measured with a chemical shift-based MRI fat-water separation method, using single-voxel MR spectroscopy (MRS) as a reference standard.
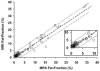
Materials and methods: In 42 patients, two repeated measurements were made using a T(1) -independent, T 2*-corrected chemical shift-based fat-water separation method with multi-peak spectral modeling of fat, and T(2) -corrected single voxel MR spectroscopy. Precision was assessed through calculation of Bland-Altman plots and concordance correlation intervals. Accuracy was assessed through linear regression between MRI and MRS. Sensitivity and specificity of MRI fat-fractions for diagnosis of steatosis using MRS as a reference standard were also calculated.
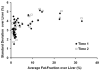
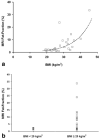
Results: Statistical analysis demonstrated excellent precision of MRI and MRS fat-fractions, indicated by 95% confidence intervals (units of absolute percent) of [-2.66%,2.64%] for single MRI ROI measurements, [-0.81%,0.80%] for averaged MRI ROI, and [-2.70%,2.87%] for single-voxel MRS. Linear regression between MRI and MRS indicated that the MRI method is highly accurate. Sensitivity and specificity for detection of steatosis using averaged MRI ROI were 100% and 94%, respectively. The relationship between hepatic fat-fraction and body mass index was examined.
Conclusion: Fat-fraction measured with T(1) -independent T 2*-corrected MRI and multi-peak spectral modeling of fat is a highly precise and accurate method of quantifying hepatic steatosis.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures





References
-
- Sass DA, Chang P, Chopra KB. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a clinical review. Dig Dis Sci. 2005;50:171–180. - PubMed
-
- Harrison SA, Neuschwander-Tetri BA. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Clin Liver Dis. 2004;8:861–879. ix. - PubMed
-
- Marchesini G, Brizi M, Bianchi G, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a feature of the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes. 2001;50:1844–1850. - PubMed
-
- Marchesini G, Brizi M, Morselli-Labate AM, et al. Association of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease with insulin resistance. Am J Med. 1999;107:450–455. - PubMed
-
- Brunt EM. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Semin Liver Dis. 2004;24:3–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

