Associations of pretransplant serum albumin with post-transplant outcomes in kidney transplant recipients
- PMID: 21449945
- PMCID: PMC3083471
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2011.03480.x
Associations of pretransplant serum albumin with post-transplant outcomes in kidney transplant recipients
Abstract
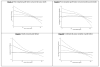
The association between pretransplant serum albumin concentration and post-transplant outcomes in kidney transplant recipients is unclear. We hypothesized that in transplant-waitlisted hemodialysis patients, lower serum albumin concentrations are associated with worse post-transplant outcomes. Linking the 5-year patient data of a large dialysis organization (DaVita) to the Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients, we identified 8961 hemodialysis patients who underwent first kidney transplantation. Mortality or graft failure and delayed graft function (DGF) risks were estimated by Cox regression (hazard ratio [HR]) and logistic regression (Odds ratio [OR]), respectively. Patients were 48 ± 13 years old and included 37% women and 27% diabetics. The higher pretransplant serum albumin was associated with lower mortality, graft failure and DGF risk even after multivariate adjustment for case-mix, malnutrition-inflammation complex and transplant related variable. Every 0.2 g/dL higher pretransplant serum albumin concentration was associated with 13% lower all-cause mortality (HR = 0.87 [95% confidence interval: 0.82-0.93]), 17% lower cardiovascular mortality (HR = 0.83[0.74-0.93]), 7% lower combined risk of death or graft failure (HR = 0.93[0.89-0.97]) and 4% lower DGF risk (OR = 0.96[0.93-0.99]). Hence, lower pretransplant serum albumin level is associated with worse post-transplant outcomes. Clinical trials to examine interventions to improve nutritional status in transplant-waitlisted hemodialysis patients and their impacts on post-transplant outcomes are indicated.
©2011 The Authors Journal compilation©2011 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Comment in
-
Transplantation: Low serum albumin associated with worse transplant outcome.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2011 Jun;7(6):302. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2011.46. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2011. PMID: 21625200 No abstract available.
References
-
- Wolfe RA, Ashby VB, Milford EL, Ojo AO, Ettenger RE, Agodoa LY, et al. Comparison of mortality in all patients on dialysis, patients on dialysis awaiting transplantation, and recipients of a first cadaveric transplant. The New England journal of medicine. 1999;341(23):1725–1730. - PubMed
-
- Schnuelle P, Lorenz D, Trede M, Van Der Woude FJ. Impact of renal cadaveric transplantation on survival in end-stage renal failure: evidence for reduced mortality risk compared with hemodialysis during long-term follow-up. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1998;9(11):2135–2141. - PubMed
-
- Port FK, Wolfe RA, Mauger EA, Berling DP, Jiang K. Comparison of survival probabilities for dialysis patients vs cadaveric renal transplant recipients. Jama. 1993;270(11):1339–1343. - PubMed
-
- Ojo AO, Port FK, Wolfe RA, Mauger EA, Williams L, Berling DP. Comparative mortality risks of chronic dialysis and cadaveric transplantation in black end-stage renal disease patients. Am J Kidney Dis. 1994;24(1):59–64. - PubMed
-
- Herzog CA, Ma JZ, Collins AJ. Long-term survival of renal transplant recipients in the United States after acute myocardial infarction. Am J Kidney Dis. 2000;36(1):145–152. - PubMed

