Distinct pharmacological and functional properties of NMDA receptors in mouse cortical astrocytes
- PMID: 21449975
- PMCID: PMC3166701
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01374.x
Distinct pharmacological and functional properties of NMDA receptors in mouse cortical astrocytes
Abstract
Background and purpose: Astrocytes of the mouse neocortex express functional NMDA receptors, which are not blocked by Mg(2+) ions. However, the pharmacological profile of glial NMDA receptors and their subunit composition is far from complete.
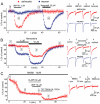
Experimental approach: We tested the sensitivity of NMDA receptor-mediated currents to the novel GluN2C/D subunit-selective antagonist UBP141 in mouse cortical astrocytes and neurons. We also examined the effect of memantine, an antagonist that has substantially different affinities for GluN2A/B and GluN2C/d-containing receptors in physiological concentrations of extracellular Mg(2+).
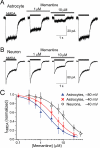
Key results: UBP141 had a strong inhibitory action on NMDA receptor-mediated transmembrane currents in the cortical layer II/III astrocytes with an IC(50) of 2.29 µM and a modest inhibitory action on NMDA-responses in the pyramidal neurons with IC(50) of 19.8 µM. Astroglial and neuronal NMDA receptors exhibited different sensitivities to memantine with IC(50) values of 2.19 and 10.8 µM, respectively. Consistent with pharmacological differences between astroglial and neuronal NMDA receptors, NMDA receptors in astrocytes showed lower Ca(2+) permeability than neuronal receptors with P(Ca) /P(Na) ratio of 3.4.
Conclusions and implications: The biophysical and pharmacological properties of the astrocytic NMDA receptors strongly suggest that they have a tri-heteromeric structure composed of GluN1, GluN2C/D and GluN3 subunits. The substantial difference between astroglial and neuronal NMDA receptors in their sensitivity to UBP141 and memantine may enable selective modulation of astrocytic signalling that could be very helpful for elucidating the mechanisms of neuron-glia communications. Our results may also provide the basis for the development of novel therapeutic agents specifically targeting glial signalling.
© 2011 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2011 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures





Similar articles
-
NMDA receptors mediate neuron-to-glia signaling in mouse cortical astrocytes.J Neurosci. 2006 Mar 8;26(10):2673-83. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4689-05.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16525046 Free PMC article.
-
Role of neuronal NR2B subunit-containing NMDA receptor-mediated Ca2+ influx and astrocytic activation in cultured mouse cortical neurons and astrocytes.Synapse. 2006 Jan;59(1):10-7. doi: 10.1002/syn.20213. Synapse. 2006. PMID: 16235228
-
Stimulation of glutamine synthetase activity by excitatory amino acids in astrocyte cultures derived from aged mouse cerebral hemispheres may be associated with non-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor activation.Int J Dev Neurosci. 1996 Jul;14(4):523-30. doi: 10.1016/0736-5748(95)00098-4. Int J Dev Neurosci. 1996. PMID: 8884386
-
Ionotropic NMDA and P2X1/5 receptors mediate synaptically induced Ca2+ signalling in cortical astrocytes.Cell Calcium. 2010 Oct;48(4):225-31. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2010.09.004. Cell Calcium. 2010. PMID: 20926134
-
NMDA Receptors in Astrocytes.Neurochem Res. 2020 Jan;45(1):122-133. doi: 10.1007/s11064-019-02750-3. Epub 2019 Feb 14. Neurochem Res. 2020. PMID: 30767094 Review.
Cited by
-
Protein quality control of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Jul 22;16:907560. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.907560. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35936491 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of Astrocytes in Alzheimer's Disease from a Neuroinflammatory and Oxidative Stress Perspective.Front Mol Neurosci. 2017 Dec 19;10:427. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2017.00427. eCollection 2017. Front Mol Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29311817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perinatal Fentanyl Exposure Leads to Long-Lasting Impairments in Somatosensory Circuit Function and Behavior.J Neurosci. 2021 Apr 14;41(15):3400-3417. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2470-20.2020. J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33853934 Free PMC article.
-
Memantine and Ibuprofen pretreatment exerts anti-inflammatory effect against streptozotocin-induced astroglial inflammation via modulation of NMDA receptor-associated downstream calcium ion signaling.Inflammopharmacology. 2021 Feb;29(1):183-192. doi: 10.1007/s10787-020-00760-0. Epub 2020 Oct 7. Inflammopharmacology. 2021. PMID: 33026572
-
NMDA receptors containing GluN2C and GluN2D subunits have opposing roles in modulating neuronal oscillations; potential mechanism for bidirectional feedback.Brain Res. 2020 Jan 15;1727:146571. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2019.146571. Epub 2019 Nov 28. Brain Res. 2020. PMID: 31786200 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

