Uncoupling p53 functions in radiation-induced intestinal damage via PUMA and p21
- PMID: 21450905
- PMCID: PMC3096742
- DOI: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-11-0052
Uncoupling p53 functions in radiation-induced intestinal damage via PUMA and p21
Abstract
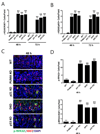
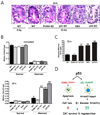
The role of p53 in tissue protection is not well understood. Loss of p53 blocks apoptosis in the intestinal crypts following irradiation but paradoxically accelerates gastrointestinal (GI) damage and death. PUMA and p21 are the major mediators of p53-dependent apoptosis and cell-cycle checkpoints, respectively. To better understand these two arms of p53 response in radiation-induced GI damage, we compared animal survival, as well as apoptosis, proliferation, cell-cycle progression, DNA damage, and regeneration in the crypts of WT, p53 knockout (KO), PUMA KO, p21 KO, and p21/PUMA double KO (DKO) mice in a whole body irradiation model. Deficiency in p53 or p21 led to shortened survival but accelerated crypt regeneration associated with massive nonapoptotic cell death. Nonapoptotic cell death is characterized by aberrant cell-cycle progression, persistent DNA damage, rampant replication stress, and genome instability. PUMA deficiency alone enhanced survival and crypt regeneration by blocking apoptosis but failed to rescue delayed nonapoptotic crypt death or shortened survival in p21 KO mice. These studies help to better understand p53 functions in tissue injury and regeneration and to potentially improve strategies to protect or mitigate intestinal damage induced by radiation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
p53 efficiently suppresses tumor development in the complete absence of its cell-cycle inhibitory and proapoptotic effectors p21, Puma, and Noxa.Cell Rep. 2013 May 30;3(5):1339-45. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.04.012. Epub 2013 May 9. Cell Rep. 2013. PMID: 23665218
-
Inhibition of CDK4/6 protects against radiation-induced intestinal injury in mice.J Clin Invest. 2016 Nov 1;126(11):4076-4087. doi: 10.1172/JCI88410. Epub 2016 Oct 4. J Clin Invest. 2016. PMID: 27701148 Free PMC article.
-
Combined loss of PUMA and p21 accelerates c-MYC-driven lymphoma development considerably less than loss of one allele of p53.Oncogene. 2016 Jul 21;35(29):3866-71. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.457. Epub 2015 Dec 7. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 26640149
-
The role of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 in apoptosis.Mol Cancer Ther. 2002 Jun;1(8):639-49. Mol Cancer Ther. 2002. PMID: 12479224 Review.
-
Protective mechanisms of p53-p21-pRb proteins against DNA damage-induced cell death.Cell Cycle. 2008 Feb 1;7(3):277-82. doi: 10.4161/cc.7.3.5328. Epub 2007 Nov 18. Cell Cycle. 2008. PMID: 18235223 Review.
Cited by
-
Assessing the radiation response of lung cancer with different gene mutations using genetically engineered mice.Front Oncol. 2013 Apr 2;3:72. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2013.00072. eCollection 2013. Front Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23565506 Free PMC article.
-
ADAR1 is essential for intestinal homeostasis and stem cell maintenance.Cell Death Dis. 2013 Apr 18;4(4):e599. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.125. Cell Death Dis. 2013. PMID: 23598411 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and radioprotective effects of novel hybrid compounds containing edaravone analogue and 3-n-butylphthalide ring-opening derivatives.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Jun;25(12):5470-5485. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16557. Epub 2021 May 8. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33963805 Free PMC article.
-
Reducing radiation-induced gastrointestinal toxicity - the role of the PHD/HIF axis.J Clin Invest. 2016 Oct 3;126(10):3708-3715. doi: 10.1172/JCI84432. Epub 2016 Aug 22. J Clin Invest. 2016. PMID: 27548524 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Paradoxical Roles of Elongation Factor-2 Kinase in Stem Cell Survival.J Biol Chem. 2016 Sep 9;291(37):19545-57. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.724856. Epub 2016 Jul 27. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27466362 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Potten CS. Radiation, the ideal cytotoxic agent for studying the cell biology of tissues such as the small intestine. Radiat Res. 2004 Feb;161(2):123–136. - PubMed
-
- Terry NH, Travis EL. The influence of bone marrow depletion on intestinal radiation damage. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1989 Sep;17(3):569–573. - PubMed
-
- Harper JW, Elledge SJ. The DNA damage response: ten years after. Mol Cell. 2007 Dec 14;28(5):739–745. - PubMed
-
- Weissman IL. Stem cells: units of development, units of regeneration, and units in evolution. Cell. 2000 Jan 7;100(1):157–168. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

