The international workshop on meibomian gland dysfunction: report of the diagnosis subcommittee
- PMID: 21450918
- PMCID: PMC3072162
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.10-6997f
The international workshop on meibomian gland dysfunction: report of the diagnosis subcommittee
Figures

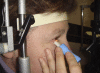
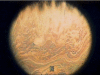


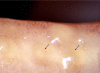



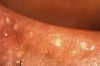
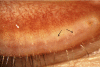


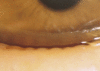

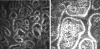


References
-
- Foulks G, Bron AJ. A clinical description of meibomian gland dysfunction. Ocul Surf. 2003;1:107–126 - PubMed
-
- Kozak I, Bron AJ, Kucharova K, et al. Morphologic and volumetric studies of the meibomian glands in elderly human eyelids. Cornea. 2007;26:610–614 - PubMed
-
- Arita R, Itoh K, Inoue K, Amano S. Noncontact infrared meibography to document age-related changes of the Meibomian glands in a normal population. Ophthalmology. 2008;115:911–915 - PubMed
-
- Nicolaides N, Kaitaranta JK, Rawdah TN, Macy JI, Boswell FM, 3rd, Smith RE. Meibomian gland studies: comparison of steer and human lipids. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1981;20:522–536 - PubMed
-
- Chew CKS, Hykin PG, Jansweijer C, Dikstein S, Tiffany JM, Bron AJ. The casual level of meibomian lipids in humans. Curr Eye Res. 1993;12:255–259 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

