Importance of two Enterococcus faecium loci encoding Gls-like proteins for in vitro bile salts stress response and virulence
- PMID: 21451003
- PMCID: PMC3107556
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiq160
Importance of two Enterococcus faecium loci encoding Gls-like proteins for in vitro bile salts stress response and virulence
Abstract
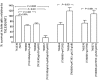
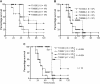
General stress proteins, Gls24 and GlsB, were previously shown to be involved in bile salts resistance of Enterococcus faecalis and in virulence. Here, we identified 2 gene clusters in Enterococcus faecium each encoding a homolog of Gls24 (Gls33 and Gls20; designated on the basis of their predicted sizes) and of GlsB (GlsB and GlsB1). The sequences of the gls33 and gls20 gene clusters from available genomes indicate distinct lineages, with those of hospital-associated CC17 isolates differing from non-CC17 by ∼7% and ∼3.5%, respectively. Deletion of an individual locus did not have a significant effect on virulence in a mouse peritonitis model, whereas a double-deletion mutant was highly attenuated (P<.004) versus wild-type. However, mutants lacking either gls33-glsB, gls20-glsB1, or both all exhibited increased sensitivity to bile salts. These results suggest that gls-encoded loci may be important for adaptation to the intestinal environment, in addition to being important for virulence functions.
© The Author 2011. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Arias CA, Murray BE. Antibiotic-resistant bugs in the 21st Century–a clinical super-challenge. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:439–43. - PubMed
-
- Hidron AI, Edwards JR, Patel J, et al. NHSN annual update: antimicrobial-resistant pathogens associated with healthcare-associated infections: annual summary of data reported to the National Healthcare Safety Network at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2006–2007. Erratum in Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2009;30:107. - PubMed
-
- Werner G, Coque TM, Hammerum AM, et al. Emergence and spread of vancomycin resistance among enterococci in Europe. Euro Surveill. 2008:13. - PubMed
-
- Eliopoulos GM. Antimicrobial agents for treatment of serious infections caused by resistant Staphylococcus aureus and enterococci. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2005;24:826–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

