Modification of shirt buttons for retrospective radiation dosimetry after a radiological event
- PMID: 21451325
- PMCID: PMC3079536
- DOI: 10.1097/HP.0b013e31820153d4
Modification of shirt buttons for retrospective radiation dosimetry after a radiological event
Abstract
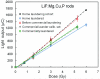
Preliminary results are presented for a personal radiation dosimeter in the form of a clothing button to provide gamma-ray dose estimation for clinically-significant external radiation exposures to the general public due to a radiological incident, such as use of a radiological dispersal device. Rods of thermoluminescent material (LiF:Mg,Ti and LiF:Mg,Cu,P) were encapsulated in plastic "buttons," attached to shirts, and subjected to three cycles of home or commercial laundering or dry cleaning, including ironing or pressing. The buttons were subsequently exposed to doses of 137Cs gamma rays ranging from 0.75 to 8.2 Gy. The rods were removed from the buttons and their light output compared to their responses when bare or to the responses of a set of calibration rods of the same type and from the same manufacturer. In all three of the comparisons for LiF:Mg,Ti rods, the relative responses of the rods in buttons changed by 2-6% relative to the same rods before cleaning. In both comparisons for LiF:Mg,Cu,P rods, the response of laundered rods was 1-3% lower than for the same rods before cleaning. Both these materials are potential candidates for button dosimeters.
Figures


References
-
- Ben Shachar B, Horowitz YS. Thermoluminescence in annealed and unannealed LiF:Mg,Ti (TLD-100, Harshaw) as a function of glow curve heating rate and using computerized glow curve deconvolution. J Phys D Appl Phys. 1992;25:694–703.
-
- Horowitz YS. The Annealing Characteristics of LiF:Mg,Ti. Radiat Prot Dosim. 1990;30:219–230.
-
- Kitis G, Tzima A, Cai GG, Furetta C. Low-temperature (80–240° C) annealing characteristics of LiF:Mg,Cu,P. J Phys D Appl Phys. 1996;29:1601–1612.
-
- Moscovitch M. Personnel dosimetry using LiF:Mg,Cu,P. Radiat Prot Dosim. 1999;85:49–56.
-
- Moscovitch M, St John TJ, Cassata JR, Blake PK, Rotunda JE, Ramlo M, Velbeck KJ, Luo LZ. The application of LiF:Mg,Cu,P to large scale personnel dosimetry: current status and future directions. Radiat Prot Dosim. 2006;119:248–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

