A specific antibody to neuropeptide AF1 (KNEFIRFamide) recognizes a small subset of neurons in Ascaris suum: differences from Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 21452223
- PMCID: PMC4769036
- DOI: 10.1002/cne.22584
A specific antibody to neuropeptide AF1 (KNEFIRFamide) recognizes a small subset of neurons in Ascaris suum: differences from Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
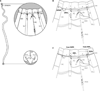
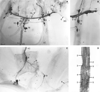
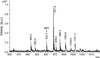
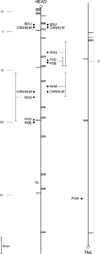
A monoclonal antibody, AF1-003, highly specific to the Ascaris suum neuropeptide AF1 (KNEFIRFamide), was generated. This antibody binds strongly to AF1 and extremely weakly to other peptides with C-terminal FIRFamide: AF5 (SGKPTFIRFamide), AF6 (FIRFamide), and AF7 (AGPRFIRFamide). It does not recognize 35 other AF (A. suum FMRFamide-like) peptides at the highest concentration tested, nor does it recognize FMRFamide. When crude peptide extracts of A. suum are fractionated by two-step HPLC, the only fractions recognized by AF1-003 are those comigrating with synthetic AF1. By immunocytochemistry, antibody AF1-003 recognizes a small subset of the 298 neurons of A. suum: these include the paired URX and RIP neurons, two pairs of lateral ganglion neurons in the head, and the unpaired PQR and PDA or -B tail neurons that send processes to the head along the dorsal and ventral nerve cords, respectively. AF1 immunoreactivity is also seen in three pairs of pharyngeal neurons. Mass spectroscopy (MS) shows the presence of AF1 in the head, pharynx, and dorsal and ventral nerve cords. In A. suum, the neurons that contain AF1 show little overlap with neurons that express green fluorescent protein constructs targeting the flp-8 gene, which encodes AF1 in Caenorhabditis elegans (Kim and Li [2004] J. Comp. Neurol. 475:540-550); the URX neurons express AF1 in both species, but, in C. elegans, flp-8 expression was not detected in RIP, PQR, and PDA or -B or in the pharynx. Other, less specific monoclonal antibodies recognize AF1, as well as other peptides to differing degrees; these antibodies are useful reagents for determination of neuronal morphology.
Copyright © 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures




References
-
- Berman ES, Fortson SL, Checchi KD, Wu L, Felton JS, Wu KJ, Kulp KS. Preparation of single cells for imaging/profiling mass spectrometry. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2008;19:1230–1236. - PubMed
-
- Brownlee DJA, Fairweather I. Exploring the neurotransmitter labyrinth in nematodes. Trends Neurosci. 1999;22:16–24. - PubMed
-
- Brownlee DJA, Walker RJ. Actions of nematode FMRFa-miderelated peptides on the pharyngeal muscle of the parasitic nematode, Ascaris suum . Ann NY Acad Sci. 1999;897:228–238. - PubMed
-
- Brownlee DJA, Fairweather I, Johnston CF, Smart D, Shaw C, Halton DW. Immunocytochemical demonstration of neuropeptides in the central nervous system of the round-worm, Ascaris suum (Nematoda, Ascaroidea) Parasitology. 1993;106:305–316. - PubMed
-
- Cowden C, Stretton AOW. AF2, an Ascaris neuropeptide: isolation, sequence, and bioactivity. Peptides. 1993;14:423–430. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

