Significant survival improvement of patients with recurrent breast cancer in the periods 2001-2008 vs. 1992-2000
- PMID: 21453503
- PMCID: PMC3080832
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-118
Significant survival improvement of patients with recurrent breast cancer in the periods 2001-2008 vs. 1992-2000
Abstract
Background: It is unclear whether individualized treatments based on biological factors have improved the prognosis of recurrent breast cancer. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the survival improvement of patients with recurrent breast cancer after the introduction of third generation aromatase inhibitors (AIs) and trastuzumab.
Methods: A total of 407 patients who received first diagnosis of recurrent breast cancer and treatment at National Kyushu Cancer Center between 1992 and 2008 were retrospectively evaluated. As AIs and trastuzumab were approved for clinical use in Japan in 2001, the patients were divided into two time cohorts depending on whether the cancer recurred before or after 2001. Cohort A: 170 patients who were diagnosed between 1992 and 2000. Cohort B: 237 patients who were diagnosed between 2001 and 2008. Tumor characteristics, treatments, and outcome were compared.
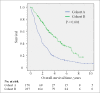
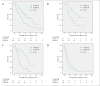
Results: Fourteen percent of cohort A and 76% of cohort B received AIs and/or trastuzumab (P < 0.001). The median overall survival (OS) times after breast cancer recurrence were 1.7 years and 4.2 years for these respective cohorts (P < 0.001). Both the time period and treatment of AIs and/or trastuzumab for recurrent disease were significant prognostic factors in multivariate analysis (cohort B vs. cohort A: HR = 0.70, P = 0.01; AIs and/or trastuzumab for recurrent disease: yes vs. no: HR = 0.46, P < 0.001). When patients were categorized into 4 subgroups by the expression of hormone receptor (HR) and HER-2 status, the median OS times of the HR-positive/HER-2-negative, HR-positive/HER-2-positive, HR-negative/HER-2-positive, and HR-negative/HER-2-negative subtypes were 2.2, 2.4, 1.6, and 1.0 years in cohort A and 4.5, 5.1, 5.0, and 1.4 years in cohort B.
Conclusions: The prognosis of patients with recurrent breast cancer was improved over time following the introduction of AIs and trastuzumab and the survival improvement was apparent in HR- and/or HER-2-positive tumors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Duration of anti-HER2 blockage therapy may improve survival in HER2 positive metastatic breast carcinoma patients.J BUON. 2013 Jul-Sep;18(3):585-93. J BUON. 2013. PMID: 24065468
-
Adding hormonal therapy to chemotherapy and trastuzumab improves prognosis in patients with hormone receptor-positive and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive primary breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013 Jan;137(2):523-31. doi: 10.1007/s10549-012-2336-6. Epub 2012 Nov 27. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013. PMID: 23184079 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment outcome and prognostic factors for patients with bone-only metastases of breast cancer: a single-institution retrospective analysis.Oncologist. 2011;16(2):155-64. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2010-0350. Epub 2011 Jan 25. Oncologist. 2011. PMID: 21266401 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and toxicity of extended aromatase inhibitors after adjuvant aromatase inhibitors-containing therapy for hormone-receptor-positive breast cancer: a literature-based meta-analysis of randomized trials.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2020 Jan;179(2):275-285. doi: 10.1007/s10549-019-05464-w. Epub 2019 Oct 12. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2020. PMID: 31606823 Review.
-
Trastuzumab for patients with HER2 positive breast cancer: delivery, duration and combination therapies.Breast. 2013 Aug;22 Suppl 2:S152-5. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2013.07.029. Breast. 2013. PMID: 24074778 Review.
Cited by
-
Temporal trends in the surgical outcomes of patients with breast cancer.World J Surg Oncol. 2012 Jun 14;10:108. doi: 10.1186/1477-7819-10-108. World J Surg Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22697184 Free PMC article.
-
Change in Survival in Metastatic Breast Cancer with Treatment Advances: Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review.JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2018 Nov;2(4):pky062. doi: 10.1093/jncics/pky062. Epub 2018 Dec 24. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2018. PMID: 30627694 Free PMC article.
-
Lymph node metastasis and high serum CEA are important prognostic factors in hormone receptor positive and HER2 negative breast cancer.Mol Clin Oncol. 2018 Nov;9(5):566-574. doi: 10.3892/mco.2018.1716. Epub 2018 Sep 13. Mol Clin Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30402236 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic factors for survivals from first relapse in breast cancer patients: analysis of deceased patients.Radiat Oncol J. 2013 Dec;31(4):222-7. doi: 10.3857/roj.2013.31.4.222. Epub 2013 Dec 31. Radiat Oncol J. 2013. PMID: 24501710 Free PMC article.
-
Defining the survival benchmark for breast cancer patients with systemic relapse.Breast Cancer (Auckl). 2015 Apr 15;9:9-17. doi: 10.4137/BCBCR.S23794. eCollection 2015. Breast Cancer (Auckl). 2015. PMID: 25922577 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Coombes RC, Hall E, Gibson LJ, Paridaens R, Jassem J, Delozier T, Jones SE, Alvarez I, Bertelli G, Ortmann O. et al.A randomized trial of exemestane after two to three years of tamoxifen therapy in postmenopausal women with primary breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;350(11):1081–1092. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa040331. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Coates AS, Keshaviah A, Thurlimann B, Mouridsen H, Mauriac L, Forbes JF, Paridaens R, Castiglione-Gertsch M, Gelber RD, Colleoni M. et al.Five years of letrozole compared with tamoxifen as initial adjuvant therapy for postmenopausal women with endocrine-responsive early breast cancer: update of study BIG 1-98. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25(5):486–492. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2006.08.8617. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

