Simple flow cytometric detection of haemozoin containing leukocytes and erythrocytes for research on diagnosis, immunology and drug sensitivity testing
- PMID: 21453521
- PMCID: PMC3078904
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2875-10-74
Simple flow cytometric detection of haemozoin containing leukocytes and erythrocytes for research on diagnosis, immunology and drug sensitivity testing
Abstract
Background: Malaria pigment (haemozoin, Hz) has been the focus of diverse research efforts. However, identification of Hz-containing leukocytes or parasitized erythrocytes is usually based on microscopy, with inherent limitations. Flow cytometric detection of depolarized Side-Scatter is more accurate and its adaptation to common bench top flow cytometers might allow several applications. These can range from the ex-vivo and in-vitro detection and functional analysis of Hz-containing leukocytes to the detection of parasitized Red-Blood-Cells (pRBCs) to assess antimalarial activity.
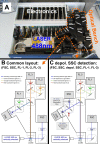
Methods: A standard benchtop flow cytometer was adapted to detect depolarized Side-Scatter. Synthetic and Plasmodium falciparum Hz were incubated with whole blood and PBMCs to detect Hz-containing leukocytes and CD16 expression on monocytes. C5BL/6 mice were infected with Plasmodium berghei ANKA or P. berghei NK65 and Hz-containing leukocytes were analysed using CD11b and Gr1 expression. Parasitized RBC from infected mice were identified using anti-Ter119 and SYBR green I and were analysed for depolarized Side Scatter. A highly depolarizing RBC population was monitored in an in-vitro culture incubated with chloroquine or quinine.
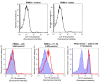
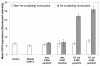
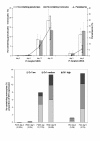
Results: A flow cytometer can be easily adapted to detect depolarized Side-Scatter and thus, intracellular Hz. The detection and counting of Hz containing leukocytes in fresh human or mouse blood, as well as in leukocytes from in-vitro experiments was rapid and easy. Analysis of CD14/CD16 and CD11b/Gr1 monocyte expression in human or mouse blood, in a mixed populations of Hz-containing and non-containing monocytes, appears to show distinct patterns in both types of cells. Hz-containing pRBC and different maturation stages could be detected in blood from infected mice. The analysis of a highly depolarizing population that contained mature pRBC allowed to assess the effect of chloroquine and quinine after only 2 and 4 hours, respectively.
Conclusions: A simple modification of a flow cytometer allows for rapid and reliable detection and quantification of Hz-containing leukocytes and the analysis of differential surface marker expression in the same sample of Hz-containing versus non-Hz-containing leukocytes. Importantly, it distinguishes different maturation stages of parasitized RBC and may be the basis of a rapid no-added-reagent drug sensitivity assay.
Figures




References
-
- Hänscheid T, Egan TJ, Grobusch MP. Hemozoin: from melatonin pigment to drug target, diagnostic tool, and immune modulator. Lancet Infect Dis. 2007;7:675–685. - PubMed
-
- Kremsner PG, Valim C, Missinou MA, Olola C, Krishna S, Issifou S, Kombila M, Bwanaisa L, Mithwani S, Newton CR, Agbenyega T, Pinder M, Bojang K, Wypij D, Taylor T. Prognostic value of circulating pigmented cells in african children with malaria. J Infect Dis. 2009;199:142–150. doi: 10.1086/595295. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lawrence C, Olson JA. Birefringent hemozoin identifies malaria. Am J Clin Pathol. 1986;86:360–363. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

