High-grade, chemotherapy-resistant primary ovarian carcinoma cell lines overexpress human trophoblast cell-surface marker (Trop-2) and are highly sensitive to immunotherapy with hRS7, a humanized monoclonal anti-Trop-2 antibody
- PMID: 21453957
- PMCID: PMC3104081
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2011.03.002
High-grade, chemotherapy-resistant primary ovarian carcinoma cell lines overexpress human trophoblast cell-surface marker (Trop-2) and are highly sensitive to immunotherapy with hRS7, a humanized monoclonal anti-Trop-2 antibody
Abstract
Objective: We evaluated the expression of human trophoblast cell-surface marker (Trop-2) and the potential of hRS7, a humanized monoclonal anti-Trop-2 antibody, as a therapeutic agent against chemotherapy-resistant ovarian disease.
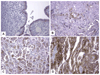
Methods: Trop-2 expression was evaluated by immunohistochemistry (IHC) in 50 ovarian serous papillary carcinoma specimens. Trop-2 expression was also evaluated by real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) and flow cytometry in a total of 6 primary ovarian cancer cell lines derived from patients with chemotherapy-resistant disease. Sensitivity to hRS7 antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) was tested in standard 5-hour ⁵¹Cr-release assays. The effect of serum and interleukin-2 (IL-2) on hRS7-mediated ADCC was also studied.
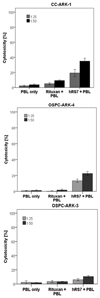
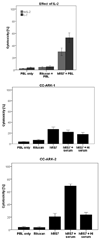
Results: Trop-2 expression was found in 41 of 50 (82%) tumor tissues tested by IHC. 83% (5 of 6) of the ovarian cancer cell lines tested by qRT-PCR and flow cytometry demonstrated high Trop-2 expression. All primary ovarian cancer cell lines expressing Trop-2 were highly sensitive to hRS7-mediated ADCC in vitro (range of killing: 19.3% to 40.8%) (p<0.001). Negligible cytotoxicity against chemotherapy-resistant ovarian cancers was seen in the absence of hRS7 or in the presence of rituximab control antibody (range of killing: 1.1% to 8.9%). Human serum did not significantly inhibit hRS7-mediated cytotoxicity while incubation with IL-2 in addition to hRS7 further increased the cytotoxic activity (p=0.04).
Conclusions: Trop-2 is highly expressed in chemotherapy-resistant ovarian cancer cell lines at mRNA and protein levels. Primary ovarian carcinoma cell lines are highly sensitive to hRS7-mediated cytotoxicity in vitro. hRS7 may represent a novel therapeutic agent for the treatment of high-grade, chemotherapy-resistant ovarian cancer.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:277–300. - PubMed
-
- Martin LP, Schilder RJ. Management of recurrent ovarian carcinoma: current status and future directions. Semin Oncol. 2009;36:112–125. - PubMed
-
- Miotti S, Canevari S, Menard S, Mezzanzanica D, Porro G, Pupa SM, et al. Characterization of human ovarian carcinoma-associated antigens defined by novel monoclonal antibodies with tumor-restricted specificity. Int J Cancer. 1987;39:297–303. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

