The relevance of tick bites to the production of IgE antibodies to the mammalian oligosaccharide galactose-α-1,3-galactose
- PMID: 21453959
- PMCID: PMC3085643
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2011.02.019
The relevance of tick bites to the production of IgE antibodies to the mammalian oligosaccharide galactose-α-1,3-galactose
Abstract
Background: In 2009, we reported a novel form of delayed anaphylaxis to red meat that is related to serum IgE antibodies to the oligosaccharide galactose-α-1,3-galactose (alpha-gal). Most of these patients had tolerated meat for many years previously. The implication is that some exposure in adult life had stimulated the production of these IgE antibodies.
Objectives: We sought to investigate possible causes of this IgE antibody response, focusing on evidence related to tick bites, which are common in the region where these reactions occur.
Methods: Serum assays were carried out with biotinylated proteins and extracts bound to a streptavidin ImmunoCAP.
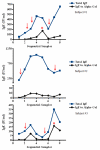
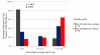
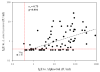
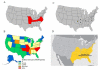
Results: Prospective studies on IgE antibodies in 3 subjects after tick bites showed an increase in levels of IgE to alpha-gal of 20-fold or greater. Other evidence included (1) a strong correlation between histories of tick bites and levels of IgE to alpha-gal (χ(2) = 26.8, P < .001), (2) evidence that these IgE antibodies are common in areas where the tick Amblyomma americanum is common, and (3) a significant correlation between IgE antibodies to alpha-gal and IgE antibodies to proteins derived from A americanum (r(s) = 0.75, P < .001).
Conclusion: The results presented here provide evidence that tick bites are a cause, possibly the only cause, of IgE specific for alpha-gal in this area of the United States. Both the number of subjects becoming sensitized and the titer of IgE antibodies to alpha-gal are striking. Here we report the first example of a response to an ectoparasite giving rise to an important form of food allergy.
Copyright © 2011 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. Published by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Bonner JA, Harari PM, Giralt J, Azarnia N, Shin DM, Cohen RB, et al. Radiotherapy plus cetuximab for squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:567–78. - PubMed
-
- Cunningham D, Humblet Y, Siena S, Khayat D, Bleiberg H, Santoro A, et al. Cetuximab monotherapy and cetuximab plus irinotecan in irinotecan-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:337–45. - PubMed
-
- O'Neil BH, Allen R, Spigel DR, Stinchcombe TE, Moore DT, Berlin JD, et al. High incidence of cetuximab-related infusion reactions in Tennessee and North Carolina; association with atopic history. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:2644–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

