Quantitative multi-compartmental SPECT image analysis for lateralization of temporal lobe epilepsy
- PMID: 21454055
- PMCID: PMC3109162
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2011.02.011
Quantitative multi-compartmental SPECT image analysis for lateralization of temporal lobe epilepsy
Abstract
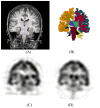
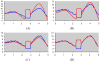
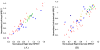
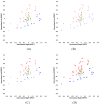
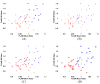
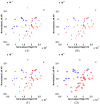
This study assesses the utility of compartmental analysis of SPECT data in lateralizing ictal onset in cases of a putative mesial temporal lobe epilepsy (mTLE). An institutional archival review provided 46 patients (18M, 28F) operated for a putative mTLE who achieved an Engel class Ia postoperative outcome. This established the standard to assure a true ictal origin. Ictal and interictal SPECT images were separately coregistered to T1-weighted (T1W) magnetic resonance (MR) image using a rigid transformation and the intensities matched with an l(1) norm minimization technique. The T1W MR image was segmented into separate structures using an atlas-based automatic segmentation technique with the hippocampi manually segmented to improve accuracy. Mean ictal-interictal intensity difference values were calculated for select subcortical structures and the accuracy of lateralization evaluated using a linear classifier. Hippocampal SPECT analysis yielded the highest lateralization accuracy (91%) followed by the amygdala (87%), putamen (67%) and thalamus (61%). Comparative FLAIR and volumetric analyses yielded 89% and 78% accuracies, respectively. A multi-modality analysis did not generate a higher accuracy (89%). A quantitative anatomically compartmented approach to SPECT analysis yields a particularly high lateralization accuracy in the case of mTLE comparable to that of quantitative FLAIR MR imaging. Hippocampal segmentation in this regard correlates well with ictal origin and shows good reliability in the preoperative analysis.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Annegers JF, Hauser WA, Coan SP, Rocca WA. A population-based study of seizures after traumatic brain injuries. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:20–24. - PubMed
-
- Aubert-Broche B, Grova C, Jannin P, Buvat I, Benali H, Gibaud B. Detection of inter-hemispheric asymmetries of brain perfusion in SPECT. Physics in Medicine and Biology. 2003;48:1505–1517. - PubMed
-
- Aubert-Broche B, Jannin P, Biraben A, Bernard AM, Haegelen C, Le Jeune FP, Gibaud B. Evaluation of methods to detect interhemispheric asymmetry on cerebral perfusion SPECT: application to epilepsy. Journal of Nuclear Medicine. 2005;46:707–713. - PubMed
-
- Avery RA, Zubal IG, Stokking R, Studholme C, Corsi M, Seibyl JP, Spencer SS. Decreased cerebral blood flow during seizures with ictal SPECT injections. Epilepsy Res. 2000;40:53–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

