Coupled ATP and potassium efflux from intercalated cells
- PMID: 21454249
- PMCID: PMC3119139
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00112.2011
Coupled ATP and potassium efflux from intercalated cells
Abstract
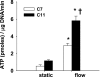
Increased flow in the distal nephron induces K secretion through the large-conductance, calcium-activated K channel (BK), which is primarily expressed in intercalated cells (IC). Since flow also increases ATP release from IC, we hypothesized that purinergic signaling has a role in shear stress (τ; 10 dynes/cm(2)) -induced, BK-dependent, K efflux. We found that 10 μM ATP led to increased IC Ca concentration, which was significantly reduced in the presence of the P(2) receptor blocker suramin or calcium-free buffer. ATP also produced BK-dependent K efflux, and IC volume decrease. Suramin inhibited τ-induced K efflux, suggesting that K efflux is at least partially dependent on purinergic signaling. BK-β4 small interfering (si) RNA, but not nontarget siRNA, decreased ATP secretion and both ATP-dependent and τ-induced K efflux. Similarly, carbenoxolone (25 μM), which blocks connexins, putative ATP pathways, blocked τ-induced K efflux and ATP secretion. Compared with BK-β4(-/-) mice, wild-type mice with high distal flows exhibited significantly more urinary ATP excretion. These data demonstrate coupled electrochemical efflux between K and ATP as part of the mechanism for τ-induced ATP release in IC.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Flow-sensitive K+-coupled ATP secretion modulates activity of the epithelial Na+ channel in the distal nephron.J Biol Chem. 2012 Nov 9;287(46):38552-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.408476. Epub 2012 Sep 21. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 23002235 Free PMC article.
-
Shear stress-induced volume decrease in C11-MDCK cells by BK-alpha/beta4.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2010 Sep;299(3):F507-16. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00222.2010. Epub 2010 Jun 24. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20576683 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and localization of BK-beta subunits in the distal nephron of the mouse kidney.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2007 Jul;293(1):F350-9. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00018.2007. Epub 2007 Apr 25. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17459953
-
Going with the flow: New insights regarding flow induced K+ secretion in the distal nephron.Physiol Rep. 2024 Oct;12(20):e70087. doi: 10.14814/phy2.70087. Physiol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39428258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An unexpected journey: conceptual evolution of mechanoregulated potassium transport in the distal nephron.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2016 Feb 15;310(4):C243-59. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00328.2015. Epub 2015 Dec 2. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26632600 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Intrinsic control of sodium excretion in the distal nephron by inhibitory purinergic regulation of the epithelial Na(+) channel.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2012 Jan;21(1):52-60. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0b013e32834db4a0. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2012. PMID: 22143248 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The mechanosensitive BKα/β1 channel localizes to cilia of principal cells in rabbit cortical collecting duct (CCD).Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2017 Jan 1;312(1):F143-F156. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00256.2016. Epub 2016 Nov 2. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2017. PMID: 27806944 Free PMC article.
-
Bicarbonate promotes BK-α/β4-mediated K excretion in the renal distal nephron.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012 Dec 1;303(11):F1563-71. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00490.2012. Epub 2012 Sep 19. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22993067 Free PMC article.
-
New perspective of ClC-Kb/2 Cl- channel physiology in the distal renal tubule.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016 May 15;310(10):F923-30. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00577.2015. Epub 2016 Jan 20. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26792067 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Flow-sensitive K+-coupled ATP secretion modulates activity of the epithelial Na+ channel in the distal nephron.J Biol Chem. 2012 Nov 9;287(46):38552-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.408476. Epub 2012 Sep 21. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 23002235 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akimova OA, Grygorczyk A, Bundey RA, Bourcier N, Gekle M, Insel PA, Orlov SN. Transient activation and delayed inhibition of Na+,K+,Cl- cotransport in ATP-treated C11-MDCK cells involve distinct P2Y receptor subtypes and signaling mechanisms. J Biol Chem 281: 31317–31325, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Anselmi F, Hernandez VH, Crispino G, Seydel A, Ortolano S, Roper SD, Kessaris N, Richardson W, Rickheit G, Filippov MA, Monyer H, Mammano F. ATP release through connexin hemichannels and gap junction transfer of second messengers propagate Ca2+ signals across the inner ear. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105: 18770–18775, 2008 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boettger T, Hubner CA, Maier H, Rust MB, Beck FX, Jentsch TJ. Deafness and renal tubular acidosis in mice lacking the K-Cl co-transporter Kcc4. Nature 416: 874–878, 2002 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

