A novel vascular disrupting agent plinabulin triggers JNK-mediated apoptosis and inhibits angiogenesis in multiple myeloma cells
- PMID: 21454451
- PMCID: PMC3110026
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2010-12-323857
A novel vascular disrupting agent plinabulin triggers JNK-mediated apoptosis and inhibits angiogenesis in multiple myeloma cells
Abstract
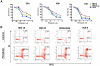
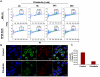
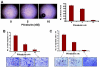
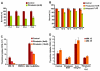
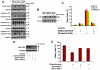
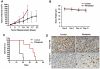
Previous studies have established a role of vascular-disrupting agents as anti- cancer agents. Plinabulin is a novel vascular-disrupting agent that exhibits potent interruption of tumor blood flow because of the disruption of tumor vascular endothelial cells, resulting in tumor necrosis. In addition, plinabulin exerts a direct action on tumor cells, resulting in apoptosis. In the present study, we examined the anti-multiple myeloma (MM) activity of plinabulin. We show that low concentrations of plinabulin exhibit a potent antiangiogenic action on vascular endothelial cells. Importantly, plinabulin also induces apoptotic cell death in MM cell lines and tumor cells from patients with MM, associated with mitotic growth arrest. Plinabulin-induced apoptosis is mediated through activation of caspase-3, caspase-8, caspase-9, and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase cleavage. Moreover, plinabulin triggered phosphorylation of stress response protein JNK, as a primary target, whereas blockade of JNK with a biochemical inhibitor or small interfering RNA strategy abrogated plinabulin-induced mitotic block or MM cell death. Finally, in vivo studies show that plinabulin was well tolerated and significantly inhibited tumor growth and prolonged survival in a human MM.1S plasmacytoma murine xenograft model. Our study therefore provides the rationale for clinical evaluation of plinabulin to improve patient outcome in MM.
Figures

References
-
- Strobeck M. Multiple myeloma therapies. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2007;6(3):181–182. - PubMed
-
- Hideshima T, Mitsiades C, Tonon G, Richardson PG, Anderson KC. Understanding multiple myeloma pathogenesis in the bone marrow to identify new therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7(8):585–598. - PubMed
-
- Dimopoulos MA, Arbuck S, Huber M, et al. Primary therapy of multiple myeloma with paclitaxel (taxol). Ann Oncol. 1994;5(8):757–759. - PubMed
-
- Miller HJ, Leong T, Khandekar JD, Greipp PR, Gertz MA, Kyle RA. Paclitaxel as the initial treatment of multiple myeloma: an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Study (E1A93). Am J Clin Oncol. 1998;21(6):553–556. - PubMed
-
- Friedenberg WR, Graham D, Greipp P, Blood E, Winston RD. The treatment of multiple myeloma with docetaxel (an ECOG study). Leuk Res. 2003;27(8):751–754. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

