The cAMP-responsive Rap1 guanine nucleotide exchange factor, Epac, induces smooth muscle relaxation by down-regulation of RhoA activity
- PMID: 21454546
- PMCID: PMC3089510
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.205062
The cAMP-responsive Rap1 guanine nucleotide exchange factor, Epac, induces smooth muscle relaxation by down-regulation of RhoA activity
Abstract
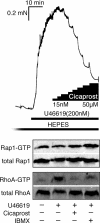
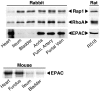
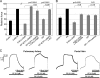
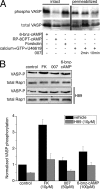
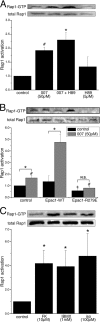
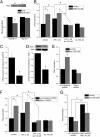
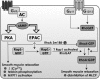
Agonist activation of the small GTPase, RhoA, and its effector Rho kinase leads to down-regulation of smooth muscle (SM) myosin light chain phosphatase activity, an increase in myosin light chain (RLC(20)) phosphorylation and force. Cyclic nucleotides can reverse this process. We report a new mechanism of cAMP-mediated relaxation through Epac, a GTP exchange factor for the small GTPase Rap1 resulting in an increase in Rap1 activity and suppression of RhoA activity. An Epac-selective cAMP analog, 8-pCPT-2'-O-Me-cAMP ("007"), significantly reduced agonist-induced contractile force, RLC(20), and myosin light chain phosphatase phosphorylation in both intact and permeabilized vascular, gut, and airway SMs independently of PKA and PKG. The vasodilator PGI(2) analog, cicaprost, increased Rap1 activity and decreased RhoA activity in intact SMs. Forskolin, phosphodiesterase inhibitor isobutylmethylxanthine, and isoproterenol also significantly increased Rap1-GTP in rat aortic SM cells. The PKA inhibitor H89 was without effect on the 007-induced increase in Rap1-GTP. Lysophosphatidic acid-induced RhoA activity was reduced by treatment with 007 in WT but not Rap1B null fibroblasts, consistent with Epac signaling through Rap1B to down-regulate RhoA activity. Isoproterenol-induced increase in Rap1 activity was inhibited by silencing Epac1 in rat aortic SM cells. Evidence is presented that cooperative cAMP activation of PKA and Epac contribute to relaxation of SM. Our findings demonstrate a cAMP-mediated signaling mechanism whereby activation of Epac results in a PKA-independent, Rap1-dependent Ca(2+) desensitization of force in SM through down-regulation of RhoA activity. Cyclic AMP inhibition of RhoA is mediated through activation of both Epac and PKA.
Figures

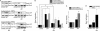
References
-
- Somlyo A. P., Somlyo A. V. (2003) Physiol. Rev. 83, 1325–1358 - PubMed
-
- Somlyo A. P., Kitazawa T., Himpens B., Matthijs G., Horiuti K., Kobayashi S., Goldman Y. E., A. V. S. (1989) Adv. Prot. Phosphatases 5, 181–195
-
- Uehata M., Ishizaki T., Satoh H., Ono T., Kawahara T., Morishita T., Tamakawa H., Yamagami K., Inui J., Maekawa M., Narumiya S. (1997) Nature 389, 990–994 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

