Positive cooperativity of the p97 AAA ATPase is critical for essential functions
- PMID: 21454554
- PMCID: PMC3091191
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.201400
Positive cooperativity of the p97 AAA ATPase is critical for essential functions
Abstract
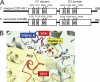
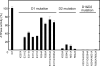
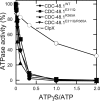
p97 is composed of two conserved AAA (ATPases associated with diverse cellular activities) domains, which form a tandem hexameric ring. We characterized the ATP hydrolysis mechanism of CDC-48.1, a p97 homolog of Caenorhabditis elegans. The ATPase activity of the N-terminal AAA domain was very low at physiological temperature, whereas the C-terminal AAA domain showed high ATPase activity in a coordinated fashion with positive cooperativity. The cooperativity and coordination are generated by different mechanisms because a noncooperative mutant still showed the coordination. Interestingly, the growth speed of yeast cells strongly related to the positive cooperativity rather than the ATPase activity itself, suggesting that the positive cooperativity is critical for the essential functions of p97.
Figures




References
-
- Ogura T., Wilkinson A. J. (2001) Genes Cells 6, 575–597 - PubMed
-
- Ammelburg M., Frickey T., Lupas A. N. (2006) J. Struct. Biol. 156, 2–11 - PubMed
-
- Latterich M., Fröhlich K. U., Schekman R. (1995) Cell 82, 885–893 - PubMed
-
- Rabouille C., Levine T. P., Peters J. M., Warren G. (1995) Cell 82, 905–914 - PubMed
-
- Patel S. K., Indig F. E., Olivieri N., Levine N. D., Latterich M. (1998) Cell 92, 611–620 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

