Architecture of a full-length retroviral integrase monomer and dimer, revealed by small angle X-ray scattering and chemical cross-linking
- PMID: 21454648
- PMCID: PMC3089549
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.212571
Architecture of a full-length retroviral integrase monomer and dimer, revealed by small angle X-ray scattering and chemical cross-linking
Abstract
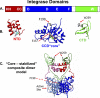
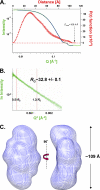
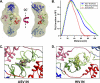
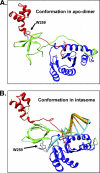
We determined the size and shape of full-length avian sarcoma virus (ASV) integrase (IN) monomers and dimers in solution using small angle x-ray scattering. The low resolution data obtained establish constraints for the relative arrangements of the three component domains in both forms. Domain organization within the small angle x-ray envelopes was determined by combining available atomic resolution data for individual domains with results from cross-linking coupled with mass spectrometry. The full-length dimer architecture so revealed is unequivocally different from that proposed from x-ray crystallographic analyses of two-domain fragments, in which interactions between the catalytic core domains play a prominent role. Core-core interactions are detected only in cross-linked IN tetramers and are required for concerted integration. The solution dimer is stabilized by C-terminal domain (CTD-CTD) interactions and by interactions of the N-terminal domain in one subunit with the core and CTD in the second subunit. These results suggest a pathway for formation of functional IN-DNA complexes that has not previously been considered and possible strategies for preventing such assembly.
Figures

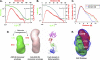


References
-
- Katz R. A., Merkel G., Kulkosky J., Leis J., Skalka A. M. (1990) Cell 63, 87–95 - PubMed
-
- Bujacz G., Jaskólski M., Alexandratos J., Wlodawer A., Merkel G., Katz R. A., Skalka A. M. (1996) Structure 4, 89–96 - PubMed
-
- Bujacz G., Alexandratos J., Wlodawer A., Merkel G., Andrake M., Katz R. A., Skalka A. M. (1997) J. Biol. Chem. 272, 18161–18168 - PubMed
-
- Maignan S., Guilloteau J. P., Zhou-Liu Q., Clément-Mella C., Mikol V. (1998) J. Mol. Biol. 282, 359–368 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

