Mutant p53 disrupts MCF-10A cell polarity in three-dimensional culture via epithelial-to-mesenchymal transitions
- PMID: 21454711
- PMCID: PMC3091229
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.214585
Mutant p53 disrupts MCF-10A cell polarity in three-dimensional culture via epithelial-to-mesenchymal transitions
Abstract
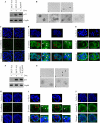
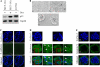
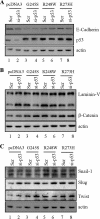
Mutant p53 is not only deficient in tumor suppression but also acquires additional activity, called gain of function. Mutant p53 gain of function is recapitulated in knock-in mice that carry one null allele and one mutant allele of the p53 gene. These knock-in mice develop aggressive tumors compared with p53-null mice. Recently, we and others showed that tumor cells carrying a mutant p53 are addicted to the mutant for cell survival and resistance to DNA damage. To further define mutant p53 gain of function, we used the MCF-10A three-dimensional model of mammary morphogenesis. MCF-10A cells in three-dimensional culture undergo a series of morphological changes and form polarized and growth-arrested spheroids with hollow lumen, which resembles normal glandular architectures in vivo. Here, we found that endogenous wild-type p53 in MCF-10A cells was not required for acinus formation, but knockdown of endogenous wild-type p53 (p53-KD) led to partial clearance of cells in the lumen due to decreased apoptosis. Consistent with this, p53-KD altered expression patterns of the cell adhesion molecule E-cadherin, the cytoskeletal marker β-catenin, and the extracellular matrix protein laminin V. We also found that ectopic expression of the mutant G245S led to a phenotype similar to p53-KD, whereas a combination of ectopic expression of siRNA-resistant G245S with p53-KD led to a less cleared lumen. In contrast, ectopic expression of mutant R248W, R175H, and R273H disrupted normal acinus architectures with filled lumen and led to formation of irregular and multiacinus structures regardless of p53-KD. In addition, these mutants altered normal expression patterns and/or levels of E-cadherin, β-catenin, laminin V, and tight junction marker ZO-1. Furthermore, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transitions (EMT) markers, Snail, Slug, and Twist, were highly induced by mutant p53 and/or p53-KD. Together, we postulate that EMT represents a mutant p53 gain of function and mutant p53 alters cell polarity via EMT.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Mutant p53 cooperates with knockdown of endogenous wild-type p53 to disrupt tubulogenesis in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 27;8(12):e85624. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085624. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24386484 Free PMC article.
-
Mammary epithelial cell polarity is regulated differentially by p73 isoforms via epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition.J Biol Chem. 2012 May 18;287(21):17746-17753. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.358143. Epub 2012 Mar 28. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22457351 Free PMC article.
-
The transcription factor Snail downregulates the tight junction components independently of E-cadherin downregulation.J Cell Sci. 2004 Apr 1;117(Pt 9):1675-85. doi: 10.1242/jcs.01004. Epub 2004 Mar 9. J Cell Sci. 2004. PMID: 15075229
-
p53 regulates cytoskeleton remodeling to suppress tumor progression.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 Nov;72(21):4077-94. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-1989-9. Epub 2015 Jul 24. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 26206378 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Opposing Roles of Wild-type and Mutant p53 in the Process of Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Jun 23;9:928399. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.928399. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35813818 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
LAMC2 enhances the metastatic potential of lung adenocarcinoma.Cell Death Differ. 2015 Aug;22(8):1341-52. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2014.228. Epub 2015 Jan 16. Cell Death Differ. 2015. PMID: 25591736 Free PMC article.
-
HuR is necessary for mammary epithelial cell proliferation and polarity at least in part via ΔNp63.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e45336. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045336. Epub 2012 Sep 18. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23028944 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial p53 Status Modifies Stromal-Epithelial Interactions During Basal-Like Breast Carcinogenesis.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2021 Jun;26(2):89-99. doi: 10.1007/s10911-020-09477-w. Epub 2021 Jan 13. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2021. PMID: 33439408 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Analysis of Cell-Cell Contact Abundance in Ovarian Carcinoma Cells Cultured in Two- and Three-Dimensional In Vitro Models.Biology (Basel). 2020 Dec 4;9(12):446. doi: 10.3390/biology9120446. Biology (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33291824 Free PMC article.
-
Isoform-specific disruption of the TP73 gene reveals a critical role for TAp73γ in tumorigenesis via leptin.Elife. 2023 Aug 31;12:e82115. doi: 10.7554/eLife.82115. Elife. 2023. PMID: 37650871 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brosh R., Rotter V. (2009) Nat. Rev. Cancer 9, 701–713 - PubMed
-
- Ko L. J., Prives C. (1996) Genes Dev. 10, 1054–1072 - PubMed
-
- Milner J., Medcalf E. A. (1991) Cell 65, 765–774 - PubMed
-
- Willis A., Jung E. J., Wakefield T., Chen X. (2004) Oncogene 23, 2330–2338 - PubMed
-
- Lang G. A., Iwakuma T., Suh Y. A., Liu G., Rao V. A., Parant J. M., Valentin-Vega Y. A., Terzian T., Caldwell L. C., Strong L. C., El-Naggar A. K., Lozano G. (2004) Cell 119, 861–872 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

