Hypoxia-inducible factor regulates expression of surfactant protein in alveolar type II cells in vitro
- PMID: 21454802
- PMCID: PMC3262688
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2011-0052OC
Hypoxia-inducible factor regulates expression of surfactant protein in alveolar type II cells in vitro
Abstract
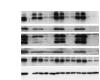
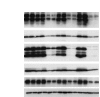
Alveolar type II (ATII) cells cultured at an air-liquid (A/L) interface maintain differentiation, but they lose these properties when they are submerged. Others showed that an oxygen tension gradient develops in the culture medium as ATII cells consume oxygen. Therefore, we wondered whether hypoxia inducible factor (HIF) signaling could explain differences in the phenotypes of ATII cells cultured under A/L interface or submerged conditions. ATII cells were isolated from male Sprague-Dawley rats and cultured on inserts coated with a mixture of rat-tail collagen and Matrigel, in medium including 5% rat serum and 10 ng/ml keratinocyte growth factor, with their apical surfaces either exposed to air or submerged. The A/L interface condition maintained the expression of surfactant proteins, whereas that expression was down-regulated under the submerged condition, and the effect was rapid and reversible. Under submerged conditions, there was an increase in HIF1α and HIF2α in nuclear extracts, mRNA levels of HIF inducible genes, vascular endothelial growth factor, glucose transporter-1 (GLUT1), and the protein level of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase isozyme-1. The expression of surfactant proteins was suppressed and GLUT1 mRNA levels were induced when cells were cultured with 1 mM dimethyloxalyl glycine. The expression of surfactant proteins was restored under submerged conditions with supplemented 60% oxygen. HIF signaling and oxygen tension at the surface of cells appears to be important in regulating the phenotype of rat ATII cells.
Figures





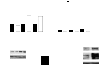
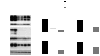

References
-
- Mason RJ. Biology of alveolar Type II cells. Respirology 2006;11:S12–S15 - PubMed
-
- Whitcutt MJ, Adler KB, Wu R. A biphasic chamber system for maintaining polarity of differentiation of cultured respiratory tract epithelial cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 1988;24:420–428 - PubMed
-
- Yamaya M, Finkbeiner WE, Chun SY, Widdicombe JH. Differentiated structure and function of cultures from human tracheal epithelium. Am J Physiol 1992;262:L713–L724 - PubMed
-
- Dobbs LG, Pian MS, Maglio M, Dumars S, Allen L. Maintenance of the differentiated Type II cell phenotype by culture with an apical air surface. Am J Physiol 1997;273:L347–L354 - PubMed
-
- Alcorn JL, Smith ME, Smith JF, Margraf LR, Mendelson CR. Primary cell culture of human Type II pneumonocytes: maintenance of a differentiated phenotype and transfection with recombinant adenoviruses. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 1997;17:672–682 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

