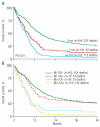
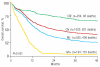
Acute myeloid leukemia with monosomal karyotype at the far end of the unfavorable prognostic spectrum
- PMID: 21454879
- PMCID: PMC3069222
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2011.043208
Acute myeloid leukemia with monosomal karyotype at the far end of the unfavorable prognostic spectrum
Figures
Comment on
-
Influence of residual normal metaphases in acute myeloid leukemia patients with monosomal karyotype.Haematologica. 2011 Apr;96(4):631-2. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2010.037838. Epub 2011 Feb 17. Haematologica. 2011. PMID: 21330329 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Lowenberg B, Downing JR, Burnett A. Acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 1999;341(14):1051–62. - PubMed
-
- Dohner H, Estey EH, Amadori S, Appelbaum FR, Buchner AK, Burnett AK, et al. Diagnosis and management of acute myeloid leukemia in adults: recommendations from an international expert panel, on behalf of the European LeukemiaNet. Blood. 2010;115(3):453–74. - PubMed
-
- Burnett A, Wetzler M, Lowenberg B. Therapeutic Advances in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(5):487–94. - PubMed
-
- Breems DA, Van Putten WL, De Greef GE, Van Zelderen-Bhola SL, Gerssen-Schoorl KBJ, Mellink CHM, et al. Monosomal karyotype in acute myeloid leukemia: a better indicator of poor prognosis than a complex karyotype. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(29):4791–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

