A conserved coatomer-related complex containing Sec13 and Seh1 dynamically associates with the vacuole in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 21454883
- PMCID: PMC3108837
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.M110.006478
A conserved coatomer-related complex containing Sec13 and Seh1 dynamically associates with the vacuole in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
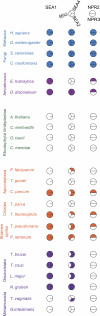
The presence of multiple membrane-bound intracellular compartments is a major feature of eukaryotic cells. Many of the proteins required for formation and maintenance of these compartments share an evolutionary history. Here, we identify the SEA (Seh1-associated) protein complex in yeast that contains the nucleoporin Seh1 and Sec13, the latter subunit of both the nuclear pore complex and the COPII coating complex. The SEA complex also contains Npr2 and Npr3 proteins (upstream regulators of TORC1 kinase) and four previously uncharacterized proteins (Sea1-Sea4). Combined computational and biochemical approaches indicate that the SEA complex proteins possess structural characteristics similar to the membrane coating complexes COPI, COPII, the nuclear pore complex, and, in particular, the related Vps class C vesicle tethering complexes HOPS and CORVET. The SEA complex dynamically associates with the vacuole in vivo. Genetic assays indicate a role for the SEA complex in intracellular trafficking, amino acid biogenesis, and response to nitrogen starvation. These data demonstrate that the SEA complex is an additional member of a family of membrane coating and vesicle tethering assemblies, extending the repertoire of protocoatomer-related complexes.
Figures





References
-
- Dacks J. B., Field M. C. (2007) Evolution of the eukaryotic membrane-trafficking system: origin, tempo and mode. J. Cell Sci. 120, 2977–2985 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 090007/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 GM083960/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR000862/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U54 RR022220/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- F32 GM088991/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM054762/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- RR00862/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM62427/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM062427/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- DP1 DA026192/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- F32 GM088991-01A1/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM54762/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- DP1DA026192/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

